Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
How does the resistance of a pure metal change if its temperature decreases?
Solution
The resistance of all pure metals increases on raising the temperature and decreases on lowering the temperature. Therefore, the resistance of a pure metal will decrease on decreasing the temperature.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
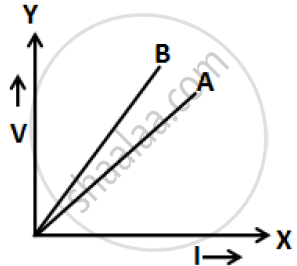
The V-I graph for a series combination and for a parallel combination of two resistors is shown in the figure below. Which of the two A or B. represents the parallel combination? Give reasons for your answer.
If five resistances, each of value 0.2 ohm, are connected in series, what will be the resultant resistance?
A p.d. of 4 V is applied to two resistors of 6 Ω and 2 Ω connected in series. Calculate:
(a) the combined resistance
(b) the current flowing
(c) the p.d. across the 6 Ω resistor
The diagram below shows part of a circuit:
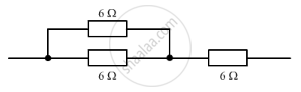
If this arrangement of three resistors was to be replaced by a single resistor, its resistance should be:
(a) 9 Ω
(b) 4 Ω
(c) 6 Ω
(d) 18 Ω
Draw a V-I graph for a conductor at two different temperatures. What conclusion do you draw from your graph for the variation of resistance of conductor with temperature?
State the order of resistivity of (i) a metal, (ii) a semiconductor and (iii) an insulator.
Six resistances are connected together as shown in the figure. Calculate the equivalent resistance between points A and B.

Two resistors of 4Ω and 6Ω are connected in parallel to a cell to draw 0.5 A current from the cell.
Draw a labelled circuit diagram showing the above arrangement.
The resistance of the hot filament of the bulb is about 10 times the cold resistance. What will be the resistance of 100 W-220 V lamps, when not in use?
