Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
How is enthalpy of sublimation related to enthalpy of fusion and enthalpy of vaporization?
Solution
Relation of enthalpy of sublimation with enthalpy of fusion and enthalpy of vaporisation:
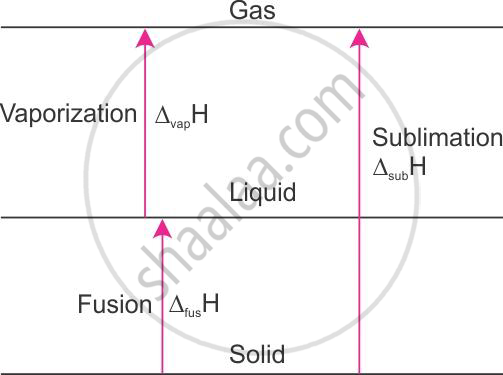
The enthalpy of sublimation of ice at 00C and 1 atm pressure is 51.08 kJ mol−1.H2O(s) → H2O(g), ΔH = 51.08 kJ mol−1 at 00C.
When solid is converted to vapour, either in one step or two steps, the solid first gets converted to the liquid state and then to the vapour state. The enthalpy change remains the same. This is because enthalpy is a state function.
For example,
H2O(s) → H2O(l), Δfus H = +6.01 kJ mol−1 at 0°C
H2O(l) → H2O(g), Δvap H = +45.07 kJ mol−1 at 0°C
_____________________________________
H2O(s) → H2O(g), Δ H = 51.08 kJ mol−1 at 0°C
Therefore, it follows that
Δsub H = Δfus H + Δvap H
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Define the Enthalpy of fusion
Define the Enthalpy of atomization
If the enthalpy of vaporisation of water at 100oC is 186.5 J.mol-1, the entropy of vaporization will be_____________ .
(a) 4.0 J . K-1. mol-1
(b) 3.0 J . K-l. mol-1
(c) 1.5 J - K-1. mol-1
(d) 0.5 J . K-l. mol-1
For a chemical reaction dS=0.035 kJ/k and dH=20kJ. At what temperature does the reaction turn nonspontaneous?
A system absorbs 640 J heat and does work of 260 J, the change in internal energy of the system will be
(a) +380J
(b) -380J
(c) +900J
(d) -900J
Define the term ‘enthalpy’.
What will happen to the internal energy if work is done by the system?
Define Enthalpy of vaporization
A system absorbs 6 kJ of heat and does 1.5 kJ of work on its surroundings. The change in internal energy is __________.
