Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
How is Total Revenue under perfect competition different from Total Revenue under imperfect competition? Give two points to show the difference.
Solution
Difference between Total Revenue under perfect competition and total revenue under imperfect competition are as follows:
| Basis of Difference | Perfect Competition | Imperfect competition |
| Dependence on Output Level | Total Revenue (TR) is precisely proportional to the quantity sold under perfect competition because the price is constant. As a result, TR increases linearly in proportion to output. | Due to the downward sloping demand curve under imperfect competition, Total Revenue (TR) is not directly proportionate to output. Firms have some pricing power and TR may rise at a slower rate, remain constant or even decrease when output increases, depending on the price elasticity of demand. |
| Impact of Price Changes | In perfect competition, a firm cannot influence price; hence, changes in total revenue are exclusively the result of changes in the quantity of goods sold. | Firms in imperfect competition can affect their product pricing through non-price competitive techniques such as marketing and product differentiation. Changes in price can have a direct impact on the firm's total revenue, both in terms of quantity sold and price per unit. The elasticity of the product demand determines the effect of a price change on overall revenue. |
| Diagram |  |
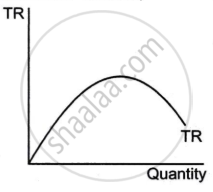 |
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What is a price taker firm?
Explain the implications of the following : Perfect knowledge in perfect competition.
Explain Perfect knowledge about the markets feature of perfect competition.
There are no barriers in the way of firms leaving or joining industry in a perfectly competitive market. Explain the significance of this feature.
Under which market form is a firm a price taker?
Why can a firm not earn abnormal profits under perfect competition in the long run? Explain.
Explain the implication of ‘freedom of entry and exit to the firms’ under perfect competition.
In which market form can a firm not influence the price of the product?
Explain how price is determined in a perfectly competitive market with fixed number of firms.
What are the characteristics of a perfectly competitive market?
How is the optimal amount of labour determined in a perfectly competitive market?
Show with the help of a diagram, how a perfectly competitive firm earns a normal profit in short-run equilibrium.
Answer the following question.
Is a firm under perfect competition a price taker, or a price maker? Justify your answer.
Choose the correct answer from given options
A firm is not a price maker under
A perfectly competitive firm always enjoys normal profit in the long run, irrespective of the situation it faces in the short run. Discuss the statement in brief.
