Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
How is the optimal amount of labour determined in a perfectly competitive market?
Solution
A profit maximising firm will employ labour up to the point where the extra cost incurred by employing the last unit of labour (wage) equals the additional benefit it earns by employing that unit of labour.
That is, Marginal cost of labour = Marginal benefit by labour
Or, Wage rate = Marginal Revenue Product
Or, w = MRPL
Or, w = MR × MPL (as MRPL = MR × MPL)
Or, w = P × MPL (in Perfect competition Price = MR)
Or, w = VMPL (because VMPL = P × MPL)
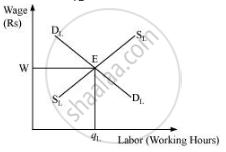
The demand for labour is derived from VMPL and the supply of labour is positively sloped. The equilibrium exists at E, where the demand for labour and the supply of labour intersect each other. The equilibrium wage rate is w and optimal amount of labour is qL.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Explain ‘large number of buyers and sellers' features of a perfectly competitive market.
Explain the implications of the following : Perfect knowledge in perfect competition.
Explain Perfect knowledge about the markets feature of perfect competition.
Under what market condition does Average Revenue always equal Marginal Revenue? Explain.
Under which market form is a firm a price taker?
Explain the implication of ‘freedom of entry and exit to the firms’ under perfect competition.
Explain how price is determined in a perfectly competitive market with fixed number of firms.
What are the characteristics of a perfectly competitive market?
Show with the help of a diagram, how a perfectly competitive firm earns a normal profit in short-run equilibrium.
Identify the market form and explain the corresponding feature, as given in the following statement:
"The commodity in this market has attributes which are identical for sellers and buyers."
Choose the correct answer from given options
A firm is not a price maker under
Under Perfect Competition, a firm will enjoy normal profit in the long run even if it enjoys supernormal profit in the short run. Explain.
Explain the short-run equilibrium of a firm facing losses under Perfect Competition.
A perfectly competitive firm always enjoys normal profit in the long run, irrespective of the situation it faces in the short run. Discuss the statement in brief.
A car company ‘W’ hired an international cricket player for its endorsement in India, while two other car companies’ ‘Y’ and ‘R’ hired two famous Bollywood film stars for this purpose. Explain the features of the competitive market indicated above.
