Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain the short-run equilibrium of a firm facing losses under Perfect Competition.
Solution
When a company suffers losses, it may be claimed that the company should not close down. Even if the company closes down in the near run, it cannot change its capital equipment and must consequently face a loss equal to the fixed cost. As a result, if the firm can make income that exceeds its variable costs, it may be able to meet its variable costs while also covering a portion of its fixed costs.
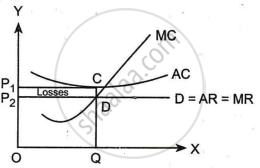
- When a company's average revenue is less than its average expense, it is considered to be losing money.
- The average cost is CQ, and the average revenue is DQ in the following figure at the current price of P2.
- Because the average cost exceeds the average revenue, the firm is said to be losing CD per unit of output. Furthermore, the overall loss on the OQ level of output equals the shaded area P1, P2, CD.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Explain ‘large number of buyers and sellers' features of a perfectly competitive market.
What is a price taker firm?
Explain the implications of the following : Perfect knowledge in perfect competition.
Under what market condition does Average Revenue always equal Marginal Revenue? Explain.
There are no barriers in the way of firms leaving or joining industry in a perfectly competitive market. Explain the significance of this feature.
Under which market form is a firm a price taker?
Explain the implication of ‘freedom of entry and exit to the firms’ under perfect competition.
In which market form can a firm not influence the price of the product?
What are the characteristics of a perfectly competitive market?
How is the optimal amount of labour determined in a perfectly competitive market?
Answer the following question.
Is a firm under perfect competition a price taker, or a price maker? Justify your answer.
Identify the market form and explain the corresponding feature, as given in the following statement:
"The commodity in this market has attributes which are identical for sellers and buyers."
Under Perfect Competition, a firm will enjoy normal profit in the long run even if it enjoys supernormal profit in the short run. Explain.
How is Total Revenue under perfect competition different from Total Revenue under imperfect competition? Give two points to show the difference.
A perfectly competitive firm always enjoys normal profit in the long run, irrespective of the situation it faces in the short run. Discuss the statement in brief.
