Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Describe the working principle of a solar cell. Mention three basic processes involved in the generation of emf.
Solution
Solar cell is a p-n junction device which works on the principle of conversion of solar energy into electrical energy by generating emf. The generation of emf by a solar cell when light falls on it is due to following three processes:
- The upper layer of p-type semiconductor is made very thin so that the incident light photons may easily reach the p-n junction.
- When the photon of light of energy greater than forbidden energy gap (
\[h\nu > E_g\]is incident on a p-n junction, electron-hole pairs are generated in the depletion layer.
- The photo-generated electrons reaching the n-side of p-n junction . The photo generated holes reaching the p-side are of p-n junction. Thus, the p-side becomes positively charged and the n-side becomes negatively charged, giving rise to photovoltage.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
When 5 V potential difference is applied across a wire of length 0.1 m, the drift speed of electrons is 2.5 x 10-4 m/s. If the electron density in the wire is 8 x 1028 m-3, calculate the resistivity of the material of the wire.
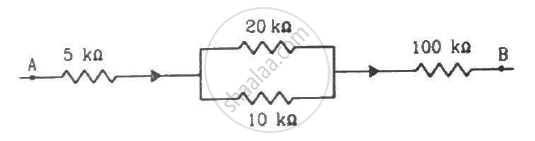
The following figure shows a part of a circuit. If a current of 12 mA exists in the 5 kΩ resistor, find the currents in the other three resistors. What is the potential difference between the points A and B?
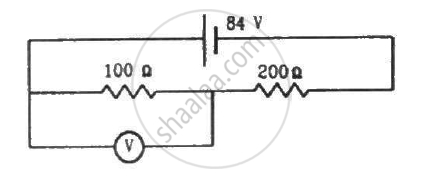
A voltmeter of resistance 400 Ω is used to measure the potential difference across the 100 Ω resistor in the circuit shown in the figure. (a) What will be the reading of the voltmeter? (b) What was the potential difference across 100 Ω before the voltmeter was connected?
A voltmeter consists of a 25 Ω coil connected in series with a 575 Ω resistor. The coil takes 10 mA for full-scale deflection. What maximum potential difference can be measured by this voltmeter?
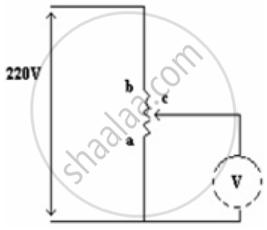
A potential difference of 220 V is maintained across 12000 Ω rheostat. Then voltmeter V has a resistance of 6000 Ω and point C is at one fourth the distance from a to b. Then the reading of voltmeter is ______.
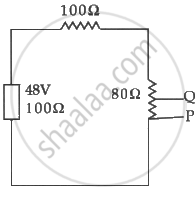
In the circuit in figure the potential difference across P and Q will be nearest to
The terminal potential difference of a cell is greater than its e.m.f when it is ______
