Commerce (English Medium)
Science (English Medium)
Arts (English Medium)
Academic Year: 2015-2016
Date & Time: 5th March 2016, 10:30 am
Duration: 3h
Advertisements
The charging current for a capacitor is 0.25 A. What is the displacement current across its plates?
Chapter: [0.08] Electromagnetic Waves
Give one example of use of eddy currents.
Chapter: [0.06] Electromagnetic Induction
Define Electric Flux. Write its SI unit.
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
A point charge Q is placed at point O as shown in the figure. The potential difference VA – VB positive. Is the charge Q negative or positive?

Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
Depict the behaviour of magnetic field lines in the presence of a diamagnetic material?
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
The wavelength λ of a photon and the de-Broglie wavelength of an electron have the same value. Show that energy of a photon in (2λmc/h) times the kinetic energy of electron; where m, c and h have their usual meaning.
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Distinguish between polarized and unpolarized light. Does the intensity of polarized light emitted by a polaroid depend on its orientation? Explain briefly.
The vibration in a beam of polarized light make an angle of 60° with the axis of the polaroid sheet. What percentage of light is transmitted through the sheet?
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
A metal rod of square cross-sectional area A having length l has current I flowing through it when a potential difference of V volt is applied across its ends (figure I). Now the rod is cut parallel to its length into two identical pieces and joined as shown in figure II. What potential difference must be maintained across the length of 2l. so that the current in the rod is still I?

Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
State Bohr postulate of hydrogen atom that gives the relationship for the frequency of emitted photon in a transition.
Chapter: [0.12] Atoms
An electron jumps from fourth to first orbit in an atom. How many maximum number of spectral lines can be emitted by the atom? To which series these lines correspond?
Chapter: [0.12] Atoms
Use de-Broglie's hypothesis to write the relation for the nth radius of Bohr orbit in terms of Bohr's quantization condition of orbital angular momentum ?
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
A device X used in communication system can convert one form of energy into another. Name the device X. Explain the function of a repeater in a communication system.
Chapter: [0.15] Communication Systems
Three rays (1, 2, 3) of different colours fall normally on one of the sides of an isosceles right angled prism as shown. The refractive index of prism for these rays is 1.39, 1.47 and 1.52 respectively. Find which of these rays get internally reflected and which get only refracted from AC. Trace the paths of rays. Justify your answer with the help of necessary calculations.
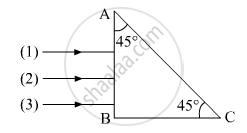
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Describe an activity to show that the colours of white light splitted by a glass prism can be recombined to get white light by another identical glass prism. Also, draw a ray diagram to show the recombination of the spectrum of white light.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Describe the working principle of a solar cell. Mention three basic processes involved in the generation of emf.
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
Why are Si and GaAs preferred materials for solar cells?
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
In the following arrangement of capacitors, the energy stored in the 6 µF capacitor is E. Find the value of the following :
(i) Energy stored in 12 µF capacitor.
(ii) Energy stored in 3 µF capacitor.
(iii) Total energy drawn from the battery.
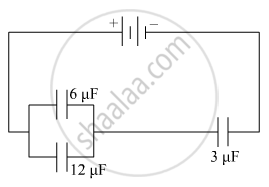
Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
Advertisements
Define 'activity' of a radioactive substance ?
Chapter: [0.13] Nuclei
Two different radioactive elements with half lives T1 and T2 have N1 and N2 undecayed atoms respectively present at a given instant. Derive an expression for the ratio of their activities at this instant in terms of N1 and N2 ?
Chapter: [0.13] Nuclei
Plot a graph showing the variation of photoelectric current with intensity of light. The work function for the following metals is given:
Na: 2.75 eV and Mo : 4.175 eV.
Which of these will not give photoelectron emission from a radiation of wavelength 3300
\[A^\circ\] from a laser beam? What happens if the source of laser beam is brought closer?
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Define the term "cut off frequency" in photoelectric emission. The threshod frequency of a metal is f. When the light of frequency 2f is incident on the metal plate, the maximum velocity of photo-electrons is v1. When the frequency of the incident radiation is increased to 5f, the maximum velocity of phto-electrons is v2. Find the ratio v1 : v2.
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Distinguish between point to point and broadcast modes of communication. Give an example of each.
Chapter: [0.15] Communication Systems
Explain the basic concept of mobile telephoning.
Chapter: [0.15] Communication Systems
Two identical coils P and Q each of radius R are lying in perpendicular planes such that they have a common centre. Find the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field at the common centre of the two coils, if they carry currents equal to I and \[\sqrt{3}\] I respectively.

Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
Define self-inductance. Write its SI units.
Chapter: [0.06] Electromagnetic Induction
A long solenoid with 15 turns per cm has a small loop of area 2.0 cm2 placed inside the solenoid normal to its axis. If the current carried by the solenoid changes steadily from 2.0 A to 4.0 A in 0.1 s, what is the induced emf in the loop while the current is changing?
Chapter: [0.06] Electromagnetic Induction
(a) Define torque acting on a dipole of dipole moment \[\vec{p}\] placed in a uniform electric field \[\vec{E}\] Express it in the vector from and point out the direction along which it acts.
(c) What would happen if the external field
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
(a) Define torque acting on a dipole of dipole moment \[\vec{p}\] placed in a uniform electric field \[\vec{E}\] Express it in the vector from and point out the direction along which it acts.
(c) What would happen if the external field
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
A point charge q moving with speed v enters a uniform magnetic field B that is acting into the plane of the paper as shown. What is the path followed by the charge q and in which plane does it move?
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
How does the path followed by the charge get affected if its velocity has a component parallel to \[\vec{B}\] .
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
If an electric field \[\vec{E}\] is also applied such that the particle continues moving along the original straight line path, what should be the magnitude and direction of the electric field \[\vec{E}\] ?
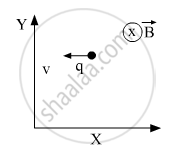
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
Which segment of electromagnetic waves has highest frequency? How are these waves produced? Give one use of these waves.
Chapter: [0.08] Electromagnetic Waves
Which em waves lie near the high frequency end of visible part of em spectrum? Give its one use. In what way this component of light has harmful effects on humans?
Chapter: [0.08] Electromagnetic Waves
Advertisements
In the following diagram, an object 'O' is placed 15 cm in front of a convex lens L1 of focal length 20 cm and the final image is formed at I at a distance of 80 cm from the second lens L2. Find the focal length of the lens L2.

Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Gautam went for a vacation to the village where his grandmother lived. His grandmother took him to watch 'nautanki' one evening. They noticed a blackbox connected to the mike lying nearby. Gautam's grandmother did not know what that box was. When she asked this question to Gautam, he explained to her that it was an amplifier.
(i) Which values were displayed by the grandmother? How can inculcation of these values in students be promoted?
(ii) What is the function of an amplifier?
(iii) Which basic electronic device is used in the amplifier?
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
A 2 µF capacitor, 100 Ω resistor and 8 H inductor are connected in series with an AC source.
(i) What should be the frequency of the source such that current drawn in the circuit is maximum? What is this frequency called?
(ii) If the peak value of e.m.f. of the source is 200 V, find the maximum current.
(iii) Draw a graph showing variation of amplitude of circuit current with changing frequency of applied voltage in a series LRC circuit for two different values of resistance R1 and R2 (R1 > R2).
(iv) Define the term 'Sharpness of Resonance'. Under what condition, does a circuit become more selective?
Chapter: [0.07] Alternating Current
With the help of a neat and labelled diagram, explain the principle and working of a moving coil galvanometer ?
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
What is the function of uniform radial field and how is it produced?
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
Define current sensitivity of a galvanometer.
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
How is current sensitivity increased?
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
In the circuit diagram given below, AB is a uniform wire of resistance 15 Ω and length 1 m. It is connected to a cell E1 of emf 2V and negligible internal resistance and a resistance R. The balance point with another cell E2 of emf 75 mV is found at 30 cm from end A. Calculate the value of R.
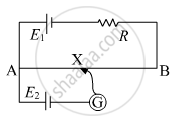
Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
Why is potentiometer preferred over a voltmeter for comparison of emf. of cells?
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
Draw a circuit diagram to determine internal resistance of a cell in the laboratory?
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
Plot a graph showing variation of voltage vs the current drawn from the cell. How can one get information from this plot about the emf of the cell and its internal resistance?
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
Two cells of emf E1 and E2 and internal resistances r1 and r2 are connected in parallel. Derive the expression for the (i) emf and (ii) internal resistance of a single equivalent cell which can replace this combination.
Chapter: [0.06] Electromagnetic Induction
State the essential conditions for diffraction of light ?
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
(i) State the essential conditions for diffraction of light.
(ii) Explain diffraction of light due to a narrow single slit and the formation of pattern of fringes on the screen.
(iii) Find the relation for width of central maximum in terms of wavelength 'λ', width of slit 'a', and separation between slit and screen 'D'.
(iv) If the width of the slit is made double the original width, how does it affect the size and intensity of the central band?
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
Draw a labelled schematic ray diagram of astronomical telescope in normal adjustment.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
Which two aberrations do objectives of refracting telescope suffer from? How are these overcome in reflecting telescope?
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
How does the resolving power of a telescope change on increasing the aperture of the objective lens? Justify your answer.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CBSE previous year question papers Class 12 Physics with solutions 2015 - 2016
Previous year Question paper for CBSE Class 12 Physics-2016 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Physics, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CBSE Class 12.
How CBSE Class 12 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Physics will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
