Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
(i) Draw a clear labelled diagram of an electric bell.
(ii) Explain in brief, its working.
(iii) What material is used for the core of an electric bell? State the reason.
Solution
(i)

(ii) An electric bell is one of the most common applications of an electromagnet.
Construction and wiring: An electric bell shown in above fig. The main parts of the bell are:
- A horse-shoe electromagnet M, having iron core,
- Soft iron armature A,
- A hammer H,
- A gong G,
- A metallic spring strip SS,
- An adjusting screw SS,
- A switch (or bell-push) K, and
- A battery.
Working and function of each part:
The working of an electric bell is based on the magnetic effect of current. When the electric circuit is closed by pressing the switch K, the current flows through the coil CC and the core of electromagnet gets magnetized and therefore it attracts the armature A as shown A, the hammer H strikes the gong G and the bell rings.
At the moment, when the armature, due to attraction, moves towards the electromagnet, the connection between the strip SS and the screw S’ breaks which stops the flow of current in the circuit. Consequently, the electromagnet loses magnetism (i.e.r it gets demagnetized) and the armature A flies back to its original position due to the spring effect of the strip SS. Now the armature again touches the screw S’, resulting in the flow of current in the circuit. The electromagnet regains its magnetism and the armature A is again attracted, so the hammer H strikes the gong G again.
This process of make and break of the circuit goes on the hammer strikes the gong repeatedly and the bell rings so long as the switch K is kept pressed.
(iii) The core of the electromagnet is made of soft iron because: Firstly, it increases the intensity of the magnetic field of the electromagnet and secondly it easily get demagnetized when no current flows in the turns of the coil of insulated copper wire wound over the core, thus helping in the smooth working of the electric bell.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Express the turn ratio in terms of voltages.
Find the ratio of primary and secondary currents in terms of turn ratio in an ideal transformer.
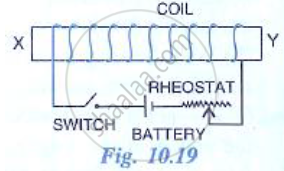
The adjacent diagram shows a coil would around a soft iron bar XY. (a) State the polarity at the end X and Y as the switch is pressed. (b) Suggest one way increasing the strength of electromagnet so formed.
Draw a labeled diagram of a full wave rectifier circuit. State its working principle. Show the input-output waveforms ?
An ideal transformer has 100 turns in the primary and 250 turns in the secondary. The peak value of the AC is 28 V. The rms secondary voltage is nearest to ______
A transformer is essentially an a.c. device. It cannot work on d.c. It changes alternating voltages or currents. It does not affect the frequency of a.c. It is based on the phenomenon of mutual induction. A transformer essentially consists of two coils of insulated copper wire having different numbers of turns and wound on the same soft iron core.
The number of turns in the primary and secondary coils of an ideal transformer is 2000 and 50 respectively. The primary coil is connected to a main supply of 120 V and secondary coil is connected to a bulb of resistance 0.6 Ω.
Power in primary coil is ______.
The primary coil of a transformer has 800 turns and the secondary coil has 8 turns. It is connected to a 220 V ac supply. What will be the output voltage?
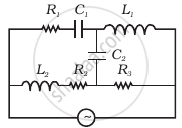
Draw the effective equivalent circuit of the circuit shown in figure, at very high frequencies and find the effective impedance.
In a transformer, number of turns in the primary coil are 140 and that in the secondary coil are 280. If current in primary coil is 4 A, then that in the secondary coil is ______.
What is a transformer?
