Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
If a light of wavelength 330 nm is incident on a metal with work function 3.55 eV, the electrons are emitted. Then the wavelength of the wave associated with the emitted electron is (Take h = 6.6 × 10–34 Js)
Options
< 2.75 × 10–9 m
≥ 2.75 × 10–9 m
≤ 2.75 × 10–12 m
< 2.5 × 10–10 m
Solution
< 2.75 × 10–9 m
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Why should gases be insulators at ordinary pressures and start conducting at very low pressures?
How does one explain the emission of electrons from a photosensitive surface with the help of Einstein's photoelectric equation?
A diode value is connected to a battery and a load resistance. The filament is heated, so that a constant current is obtained in the circuit. As the cathode continuously emits electrons, does it become more and more positively charged?
The wavelength λe of an electron and λp of a photon of same energy E are related by
Emission of electrons by the absorption of heat energy is called ____________ emission.
Why do metals have a large number of free electrons?
Define the work function of a metal. Give its unit.
Photoelectric emission is observed from a metallic surface for frequencies ν1 and ν2 of the incident light (ν1 > ν2). If the maximum value of kinetic energy of the photoelectrons emitted in the two cases are in the ration 1 : n then the threshold frequency of the metallic surface is ______.
Consider Figure for photoemission.
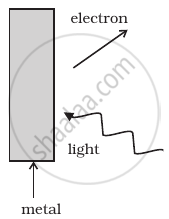
How would you reconcile with momentum conservation? Note light (photons) have momentum in a different direction than the emitted electrons.
Name the factors on which photoelectric emission from a surface depends.
