Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In a Std. X class out of 40 students 10 students use spectacles, 2 students have positive power and 8 students have negative power of lenses in their spectacles.
Answer the following questions:
(1) What does the negative power indicate?
(2) What does the positive power indicate?
(3) Generally which type of spectacles do most of the students use?
(4) What defect of eyesight do most of the students suffer from?
(5) Give two possible reasons for the above defect.
Solution
(1) The negative power indicates that the spectacles used by the students have concave lens.
(2) The positive power indicates that the spectacles used by the students have convex lens.
(3) Diverging or concave lens spectacles are generally used by the students.
(4) Most of the students suffer from the eye defect known as myopia (near sightedness).
(5) The two possible reasons for the eye defect (myopia) are
- Converging power of the eye lens becomes high as ciliary muscles do not relax sufficiently.
- Length of the eye ball increases as the distance between the eye lens and the retina increases.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Millions of people in the developing countries of the world are suffering from corneal blindness. These persons can be cured by replacing the defective cornea with the cornea of a donated eye. A charitable society of your city has organised a campaign in your neighbourhood in order to create awareness about this fact. If you are asked to participate in this mission, how would you contribute in this noble cause?
(i) State the objective of organising such campaigns.
(ii) List two arguments which you would give to motivate the people to donate their eyes after death.
(iii) List two values which are developed in the persons who actively participate and contribute in such programmes.
About 45 lac people in the developing countries are suffering from corneal blindness. About 30 lac children below the age of 12 years suffering from this defect can be cured by replacing the defective cornea with the cornea of a donated eye. How and why can students of your age involve themselves to create awareness about this fact among people?
Explain two possible reasons of myopia. How can it be corrected? Explain with a suitable diagram.
What is the other name for
hypermetropia
What is the scientific name of
short-sightedness
Name the defect of vision in which the eye-lens loses its power of accommodation due to old age.
Name the defect of vision which makes the eye-lens cloudy resulting in blurred vision.
Where is the near point of a person suffering from hypermetropia (or long-sightedness)?
A man can read the number of a distant but clearly but he finds difficulty in reading a book.
What type of spectacle lens should he use to correct the defect?
Name the defect of vision which can be corrected by a diverging lens. Show clearly by a ray diagram how the lens corrects the defect.
A person suffering from the eye-defect myopia (short-sightedness) can see clearly only up to a distance of 2 metres. What is the nature and power of lens required to rectify this defect?
What is short-sightedness? State the two causes of short-sightedness (or myopia). With the help of ray diagrams, show:
(i) the eye-defect short-sightedness.
(ii) correction of short-sightedness by using a lens.
The near point of a long-sighted person is 50 cm from the eye.
(a) Can she see clearly an object at:
(i) a distance of 20 cm?
(ii) at infinity?
A person can read a book clearly only if he holds it at an arm's length from him. Name the defect of vision:
if the person is an old man
Name the following:
The photosensitive pigment present in the rods of the retina.
Differentiate between members of the following pair with reference to what is asked in bracket.
Myopia and hyperopia (cause of the defect)
Explain the terms ‘adaptation’ and ‘accommodation’ with reference to the eye.
Enumerate the common defects of vision, their causes and the possible methods of correcting them.
Given below is a diagram depicting a defect of the human eye. Study the same and answer the question that follow:
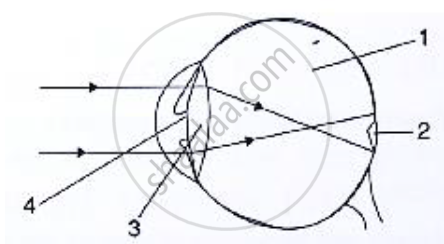
Name the defect shown in the diagram.
A person is unable to see distinctly the objects closer than 1 m. Name the defect of vision he is suffering from. Draw ray diagrams to illustrate the cause of the defect and its correction by suitable lens.
A person cannot read newspaper placed nearer than 50 cm from his eyes. Name the defect of vision he is suffering from. Draw a ray diagram to illustrate this defect. List its two possible causes. Draw a ray diagram to show how this defect may be corrected using a lens of appropriate focal length.
When do we consider a student sitting in the class to be myopic? List two causes of this defect. Explain using a ray diagram how this defect of eye can be corrected.
Given below is a diagram depicting a defect of the human eye? Study the same and answer the question that follow:

Draw a labeled diagram to show how the above mentioned defect is rectified using the lens named above.
Rewrite the following table so as to match second and third column with first column.
|
Column I
|
Column II
|
Column III
|
|
(i) Myopia
|
Old age problem
|
Bifocal lens
|
|
(ii) Presbyopia
|
Nearsightedness
|
Concave lens.
|
In what two whys is a yellow spot different from the blind spot?
Name the common defects of the eye.
Give Reason:
Older people require glasses to read and write.
Give Reason:
Deficiency of vitamin A causes night blindness.
Differentiate between:
Myopia and Hypermetropia.
Explain the Term: Cataract
Choose the Odd One Out:
In Myopia the human eye _______.
Assertion: Concave mirrors are used as reflectors in torches, vehicle head lights and in search lights.
Reason: When an object is placed beyond the center of curvature of a concave mirror, the image formed is real and inverted.
Observe the figure and answer the following questions:
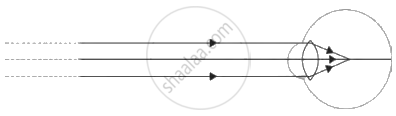
- Name the defect of vision represented in the above figure.
- State the reasons for this defect.
- How is it corrected?
- Draw the diagram to show the correction of this defect.
A person is unable to see clearly a poster fixed on a distant wall. He however sees it clearly when standing at a distance of about 2 m from the wall.
- Draw ray diagram to show the formation of image by his eye lens when he is far away from the wall.
- List two possible reasons of this defect of vision.
- Draw ray diagram to show the correction of this defect using appropriate lens.
