Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In the circuit shown in figure, find the value of RC.
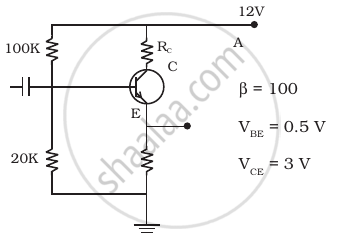
Solution
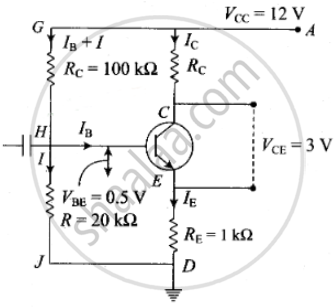
IE = IC + IB
IC = βIB
ICRC + VCE 6 IERE = VCC
RIB + VBE + IERE = VCC
From (3) Ie ≈ Ic = βIB
(R + βRE) = VCC – VBE,
IB = `(V_(C C) - V_(BE))/(R + βR_E)`
= `11.5/200` mA
From (2)
RC + RE = `(V_(C C) - V_(CE))/I_C`
= `(V_(C C) - V_(CE))/(βI_B)`
= `2/11.5 (12 - 3)` KΩ = 1.56 KΩ
RC = 1.56 – 1
= 0.56 KΩ
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
For a transistor amplifier, the voltage gain
(a) remains constant for all frequencies.
(b) is high at high and low frequencies and constant in the middle frequency range.
(c) is low at high and low frequencies and constant at mid frequencies.
(d) None of the above.
Two amplifiers are connected one after the other in series (cascaded). The first amplifier has a voltage gain of 10 and the second has a voltage gain of 20. If the input signal is 0.01 volt, calculate the output ac signal.
Explain briefly the principle on which a transistor-amplifier works as an oscillator. Draw the necessary circuit diagram and explain its working ?
Motion of hole is a convenient way of describing ______.
A transistor is
In a npn transistor circuit, the collector current is 10 mA. If 95 per cent of the electrons emitted reach the collector, which of the following statements are true?
- The emitter current will be 8 mA.
- The emitter current will be 10.53 mA.
- The base current will be 0.53 mA.
- The base current will be 2 mA.
In a CE transistor amplifier there is a current and voltage gain associated with the circuit. In other words there is a power gain. Considering power a measure of energy, does the circuit voilate conservation of energy?
