Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
For the transistor circuit shown in figure, evaluate VE, RB, RE given IC = 1 mA, VCE = 3 V, VBE = 0.5 V and VCC = 12 V, β = 100.
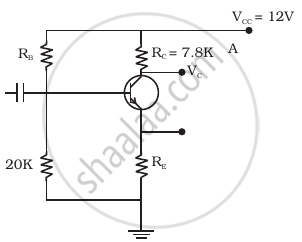
Solution
Let us redraw the circuit diagram given here to solve this problem.
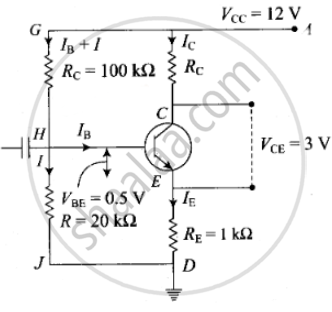
As we know the base current is very small. So,
IC = IE
RC = 7.8 kΩ
From the figure, `I_C (R_C + R_E) + V_(CE)` = 12
`(R_E + R_C) xx 1 xx 10^-3 + 3` = 12
`R_E + R_C = 9 xx 10^3 + 3` = 12
`R_E = 9 - 7.8` = 1.2 kΩ
`V_E = I_E xx R_E`
= `1 xx 10^-3 xx 1.2 xx 10^3`
= 1.2 V
Voltage VB = VE + VBE = 1.2 + 0.5 = 1.7 V
Current, I = `V_B/(20 xx 10^3) = 1.7/(20 xx 10^3)` = 0.085 mA
Resistance, RB = `(12 - 1.7)/(I_C/beta + 0.085) xx 10^3`
= `10.3/(0.01 + 0.085)` .....[Given, β = 100]
= 108 kΩ
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Draw a simple circuit of a CE transistor amplifier. Explain its working ?
Show that the voltage gain, AV, of the amplifier is given by `A_v = (beta_(ac) R_1)/r_i`where βac is the current gain, RL is the load resistance and ri is the input resistance of the transistor. What is the significance of the negative sign in the expression for the voltage gain?
Let iE, iC and iB represent the emitter current, the collector current and the base current respectively in a transistor. Then
(a) iC is slightly smaller than iE
(b) iC is slightly greater than iE
(c) iB is much smaller than iE
(d) iB is much greater than iE.
In a normal operation of a transistor,
(a) the base−emitter junction is forward-baised
(b) the base−collector junction is forward-baised
(c) the base−emitter junction is reverse-baised
(d) the base−collector junction is reverse-baised.
Draw a circuit diagram of an n-p-n transistor with its emitter-base junction forward biased and basecollector junction reverse biased. Briefly describe its working.
Explain how a transistor in its active state exhibits a low resistance at its emitter-base junction and high resistance at its base-collector junction.
Derive the expression for the voltage gain of a transistor amplifier in CE configuration in terms of the load resistance RL, current gain a βa and input resistance.
Explain why input and output voltages are in opposite phase.
Draw a circuit diagram of an n-p-n transistor with its emitter-base junction forward biased and base-collector junction reverse biased. Briefly describe its working.
Explain how a transistor in its active state exhibits a low resistance at its emitter-base junction and high resistance at its base-collector junction.
Derive the expression for the voltage gain of a transistor amplifier in CE configuration in terms of the load resistance RL, current gain βa and input resistance.
Explain why input and output voltages are in the opposite phase.
Answer the following question.
Draw the circuit arrangement for studying the output characteristics of an n-p-n transistor in CE configuration. Explain how the output characteristics is obtained.
