Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
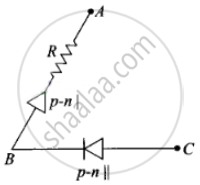
Consider a box with three terminals on top of it as shown in figure (a):
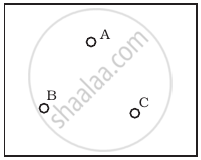 (a) |
Three components namely, two germanium diodes and one resistor are connected across these three terminals in some arrangement. A student performs an experiment in which any two of these three terminals are connected in the circuit shown in figure (b).
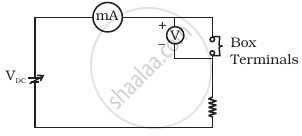 (b) |
The student obtains graphs of current-voltage characteristics for unknown combination of components between the two terminals connected in the circuit. The graphs are
(i) when A is positive and B is negative
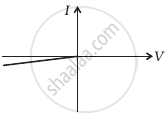 (c) |
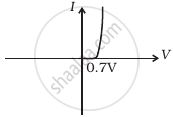
(ii) when A is negative and B is positive
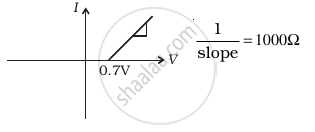 (d) |
(iii) When B is negative and C is positive
|
(e) |
(iv) When B is positive and C is negative
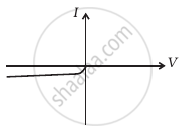 (f) |
(v) When A is positive and C is negative
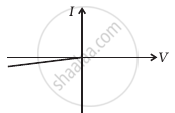 (g) |
(vi) When A is negative and C is positive
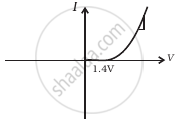 (h) |
From these graphs of current-voltage characteristics shown in figure (c) to (h), determine the arrangement of components between A, B and C.
Solution
The V-I characteristics of these graphs are discussed in points:
(a) In the V-I graph of condition (i), reverse characteristics are shown in figure (c). Here A is connected to the n-side of p-n junction I and B is connected top-side of the p-n junction I with a resistance in series.
(b) In the V-I graph of condition (ii), a forward characteristic is shown in figure (d), where 0.7 V is the knee voltage of p-n junction I. 1/slope = (1/1000) Ω.
It means A is connected to the n-side of p-n junction I and B is connected to the p-side of p-n junction I and resistance R is in a series of p-n junction I between A and B.
(c) In the V-I graph of condition (iii), a forward characteristic is shown in figure (e), where 0.7 V is the knee voltage. In this case, p-side of p-n junction II is connected to C and the n-side of p-n junction II to B.
(d) In V-I graphs of conditions (iv), (v), (vi) also concludes the above connection of p-n junctions I and II along with a resistance R.
Thus, the arrangement of p-n I, p-n II and resistance R between A, B and C will be as shown in the figure.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What happens when a forward bias is applied to a p-n junction?
Draw its I – V characteristics of photodiode
Draw a labelled diagram of a full wave rectifier. Show how output voltage varies with time if the input voltage is a sinusoidal voltage.
A plate current of 10 mA is obtained when 60 volts are applied across a diode tube. Assuming the Langmuir-Child relation \[i_p \infty V_p^{3/2}\] to hold, find the dynamic resistance rp in this operating condition.
Answer the following question.
Why photodiodes are required to operate in reverse bias? Explain.
The expected energy of the electron at absolute zero is called:-
Avalanche breakdown is due to ______.
In Figure, Vo is the potential barrier across a p-n junction, when no battery is connected across the junction ______.
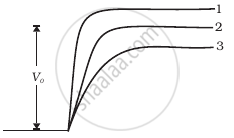
Explain the formation of the barrier potential in a p-n junction.
What is meant by forward biasing of a semiconductor diode?