Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A plate current of 10 mA is obtained when 60 volts are applied across a diode tube. Assuming the Langmuir-Child relation \[i_p \infty V_p^{3/2}\] to hold, find the dynamic resistance rp in this operating condition.
Solution
According to Lamgmuir-Child Law,
the relation between plate current (ip) and the plate voltage (Vp) is given by
\[i_p = C {V_p}^{3/2} ............(1)\]
Differentiating equation (1) with respect Vp, we get:-
\[\frac{d i_p}{d V_p} = \frac{3}{2}C {V_p}^{1/2} ............(2)\]
Dividing (2) and (1), we get:-
\[\frac{1}{i_p}\frac{d i_p}{d v_p} = \frac{3/2C {V_p}^{1/2}}{C {V_p}^{3/2}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \frac{1}{i_p} . \frac{d i_p}{d v_p} = \frac{3}{2 V_p}\]
The dynamic resistance is given by:-
\[\frac{d v_p}{d i_p} = \frac{2 V_p}{3 i_p}\]
\[ r_p = \frac{2 V_p}{3 i_p}\]
\[ r_p = \frac{2 \times 60}{3 \times 10 \times {10}^{- 3}}\]
\[ r_p = 4 \times {10}^3 = 4 k\Omega\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
(i) Explain with the help of a diagram the formation of depletion region and barrier potential in a pn junction.
With the help of neat labelled circuit diagram explain the working of half wave rectifier using semiconductor diode. Draw the input and output waveforms.
What causes the setting up of high electric field even for small reverse bias voltage across the diode?
The graph shown in the figure represents a plot of current versus voltage for a given semiconductor. Identify the region, if any, over which the semiconductor has a negative resistance.
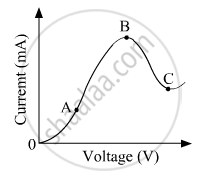
Why is a zener diode considered as a special purpose semiconductor diode?
The power delivered in the plate circular of a diode is 1.0 W when the plate voltage is 36 V. Find the power delivered if the plate voltage is increased to 49 V. Assume Langmuir-Child equation to hold.
In semiconductor physics, what is meant by:
(i) rectifier
(ii) an amplifier
(iii) an oscillator
In forward bias width of potential barrier in a p + n junction diode
The expected energy of the electron at absolute zero is called:-
On increasing the reverse biases voltage to a large value in a P – N junction diode-current
In a semiconductor diode, the barrier potential offers opposition to only
In the circuit shown in figure, if the diode forward voltage drop is 0.3 V, the voltage difference between A and B is ______.

When an electric field is applied across a semiconductor ______.
- electrons move from lower energy level to higher energy level in the conduction band.
- electrons move from higher energy level to lower energy level in the conduction band.
- holes in the valence band move from higher energy level to lower energy level.
- holes in the valence band move from lower energy level to higher energy level.
The breakdown in a reverse biased p–n junction diode is more likely to occur due to ______.
- large velocity of the minority charge carriers if the doping concentration is small.
- large velocity of the minority charge carriers if the doping concentration is large.
- strong electric field in a depletion region if the doping concentration is small.
- strong electric field in the depletion region if the doping concentration is large.
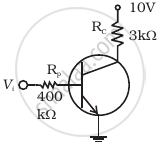
In the circuit shown in figure, when the input voltage of the base resistance is 10 V, Vbe is zero and Vce is also zero. Find the values of Ib, Ic and β.
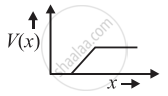
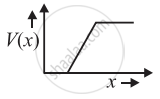
The graph of potential barrier versus width of depletion region for an unbiased diode is shown in graph A. In comparison to A, graphs B and C are obtained after biasing the diode in different ways. Identify the type of biasing in B and C and justify your answer
| ‘A’ | ‘B’ | ‘C’ |
 |
 |
 |
Draw V-I characteristics of a p-n Junction diode.
Read the following paragraph and answer the questions that follow.
| A semiconductor diode is basically a pn junction with metallic contacts provided at the ends for the application of an external voltage. It is a two-terminal device. When an external voltage is applied across a semiconductor diode such that the p-side is connected to the positive terminal of the battery and the n-side to the negative terminal, it is said to be forward-biased. When an external voltage is applied across the diode such that the n-side is positive and the p-side is negative, it is said to be reverse-biased. An ideal diode is one whose resistance in forward biasing is zero and the resistance is infinite in reverse biasing. When the diode is forward biased, it is found that beyond forward voltage called knee voltage, the conductivity is very high. When the biasing voltage is more than the knee voltage the potential barrier is overcome and the current increases rapidly with an increase in forward voltage. When the diode is reverse biased, the reverse bias voltage produces a very small current of about a few microamperes which almost remains constant with bias. This small current is a reverse saturation current. |
- In the given figure, a diode D is connected to an external resistance R = 100 Ω and an emf of 3.5 V. If the barrier potential developed across the diode is 0.5 V, the current in the circuit will be:

(a) 40 mA
(b) 20 mA
(c) 35 mA
(d) 30 mA - In which of the following figures, the pn diode is reverse biased?
(a)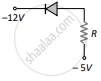
(b)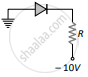
(c)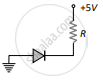
(d)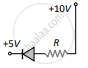
- Based on the V-I characteristics of the diode, we can classify the diode as:
(a) bilateral device
(b) ohmic device
(c) non-ohmic device
(d) passive element
OR
Two identical PN junctions can be connected in series by three different methods as shown in the figure. If the potential difference in the junctions is the same, then the correct connections will be:
(a) in the circuits (1) and (2)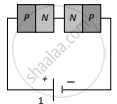
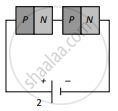
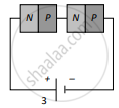
(b) in the circuits (2) and (3)
(c) in the circuits (1) and (3)
(d) only in the circuit (1) 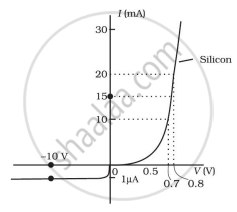
The V-I characteristic of a diode is shown in the figure. The ratio of the resistance of the diode at I = 15 mA to the resistance at V = -10 V is
(a) 100
(b) 106
(c) 10
(d) 10-6
With reference to a semiconductor diode, define the depletion region.
