Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Draw V-I characteristics of a p-n Junction diode.
Solution
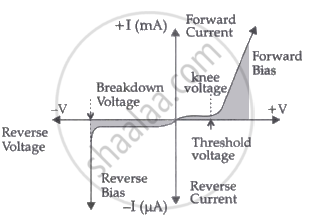
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Explain the working of P-N junction diode in forward and reverse biased mode.
What causes the setting up of high electric field even for small reverse bias voltage across the diode?
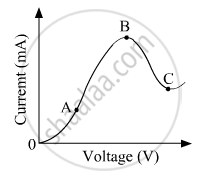
The graph shown in the figure represents a plot of current versus voltage for a given semiconductor. Identify the region, if any, over which the semiconductor has a negative resistance.
A triode value operates at Vp = 225 V and Vg = −0.5 V.
The plate current remains unchanged if the plate voltage is increased to 250 V and the grid voltage is decreased to −2.5 V. Calculate the amplification factor.
The dynamic plate resistance of a triode value is 10 kΩ. Find the change in the plate current if the plate voltage is changed from 200 V to 220 V.
With reference to a semiconductor diode, what is meant by:
(i) Forward bias
(ii) Reverse bias
(iii) Depletion region
With reference to Semiconductor Physics,
Name the diode that emits spontaneous radiation when forward biased.
The nature of binding for a crystal with alternate and evenly spaced positive and negatively ions is
When an electric field is applied across a semiconductor ______.
- electrons move from lower energy level to higher energy level in the conduction band.
- electrons move from higher energy level to lower energy level in the conduction band.
- holes in the valence band move from higher energy level to lower energy level.
- holes in the valence band move from lower energy level to higher energy level.
Draw a labelled characteristic curve (l-V graph) for a semiconductor diode during forward bias.
