Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
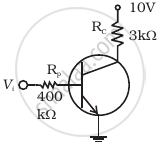
In the circuit shown in figure, when the input voltage of the base resistance is 10 V, Vbe is zero and Vce is also zero. Find the values of Ib, Ic and β.
Solution
According to the problem, Vi = 10 V, Resistance, RB = 400 kΩ, VBE = 0, VCE = 0 and RC = 3 kΩ
`V_i - V_(BE) = R_BI_B`
`I_B = ("Voltage across" R_B)/R_B`
= `10/(400 xx 10^3)`
= `25 xx 10^-6` A
= 25 μA
Voltage across RC = 10 V
`V_(CC) - V_(CE) = I_CR_C`
`I_C = ("Voltage across" R_C)/R_C`
= `10/(3 xx 10^3)`
= `3.33 xx 10^-3` A
= 3.33 mA
β = `I_C/I_B`
= `(3.33 xx 10^-3)/(25 xx 10^-6)`
= `1.33 xx 10^2`
= 133
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What happens when a forward bias is applied to a p-n junction?
When a forward bias is applied to a p-n junction, it ______.
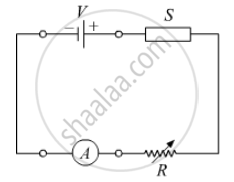
In the following diagram 'S' is a semiconductor. Would you increase or decrease the value of R to keep the reading of the ammeter A constant when S is heated? Give reason for your answer.
Plot a graph showing variation of current versus voltage for the material GaAs ?
The plate current in a diode is 20 mA when the plate voltage is 50 V or 60 V. What will be the current if the plate voltage is 70 V?
Diffusion in a p-n junction is due to ______.
A – pn junction has a depletion layer of thickness .of the order of
In the depletion region of a diode ______.
- there are no mobile charges.
- equal number of holes and electrons exist, making the region neutral.
- recombination of holes and electrons has taken place.
- immobile charged ions exist.
Explain the formation of the barrier potential in a p-n junction.
With reference to a semiconductor diode, define the potential barrier.
