Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
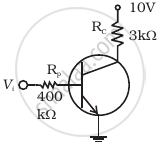
In the circuit shown in figure, when the input voltage of the base resistance is 10 V, Vbe is zero and Vce is also zero. Find the values of Ib, Ic and β.
उत्तर
According to the problem, Vi = 10 V, Resistance, RB = 400 kΩ, VBE = 0, VCE = 0 and RC = 3 kΩ
`V_i - V_(BE) = R_BI_B`
`I_B = ("Voltage across" R_B)/R_B`
= `10/(400 xx 10^3)`
= `25 xx 10^-6` A
= 25 μA
Voltage across RC = 10 V
`V_(CC) - V_(CE) = I_CR_C`
`I_C = ("Voltage across" R_C)/R_C`
= `10/(3 xx 10^3)`
= `3.33 xx 10^-3` A
= 3.33 mA
β = `I_C/I_B`
= `(3.33 xx 10^-3)/(25 xx 10^-6)`
= `1.33 xx 10^2`
= 133
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Why is a zener diode considered as a special purpose semiconductor diode?
The plate current in a diode is 20 mA when the plate voltage is 50 V or 60 V. What will be the current if the plate voltage is 70 V?
The dynamic plate resistance of a triode value is 10 kΩ. Find the change in the plate current if the plate voltage is changed from 200 V to 220 V.
What are the applications of p - n Junction diode?
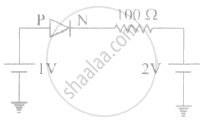
The current through an ideal PN-junction shown in the following circuit diagram will be:
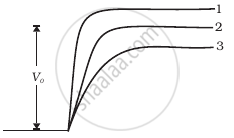
In Figure, Vo is the potential barrier across a p-n junction, when no battery is connected across the junction ______.
 (a) |
 (b) |
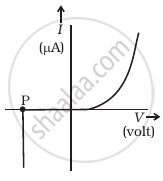
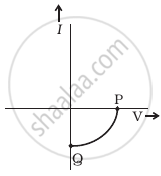
- Name the type of a diode whose characteristics are shown in figure (A) and figure (B).
- What does the point P in figure (A) represent?
- What does the points P and Q in figure (B) represent?
Explain the formation of the barrier potential in a p-n junction.
Draw the circuit arrangement for studying V-I characteristics of a p-n junction diode in (i) forward biasing and (ii) reverse biasing. Draw the typical V-I characteristics of a silicon diode.
Describe briefly the following term:
breakdown voltage in reverse biasing
