Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
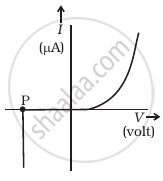 (a) |
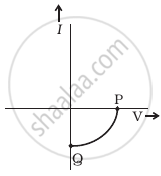 (b) |
- Name the type of a diode whose characteristics are shown in figure (A) and figure (B).
- What does the point P in figure (A) represent?
- What does the points P and Q in figure (B) represent?
उत्तर
- Figure (a) represents the characteristics of the Zener diode and curve (b) is of the solar cell.
- In figure (a), point P represents Zener breakdown voltage.
- In figure (b), point Q represents zero voltage and negative current. This means the light falling on the solar cell with at least a minimum threshold frequency gives the current in opposite direction to that due to a battery connected to solar cell. But for point Q the battery is short-circuited. Hence it represents the short circuit current. And the point Pin fig. (b) represents some open circuit, the voltage on solar cell with zero current through solar cell.
It means, there is a battery connected to a solar cell which gives rise to the equal and opposite current to that in a solar cell by virtue of light falling on it.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What happens when a forward bias is applied to a p-n junction?
Draw a labelled diagram of a full wave rectifier. Show how output voltage varies with time if the input voltage is a sinusoidal voltage.
Show on a graph, the variation of resistivity with temperature for a typical semiconductor.
With reference to semi-conductors answer the following :
(i) What is the change in the resistance of the semi-conductor with increase in temperature ?
(ii) Name the majority charge carriers in n-type semi-conductor.
(iii) What is meant by doping ?
The dynamic plate resistance of a triode value is 10 kΩ. Find the change in the plate current if the plate voltage is changed from 200 V to 220 V.
Use a transistor as an amplition
In the circuit shown in figure, if the diode forward voltage drop is 0.3 V, the voltage difference between A and B is ______.

Can the potential barrier across a p-n junction be measured by simply connecting a voltmeter across the junction?
Consider a box with three terminals on top of it as shown in figure (a):
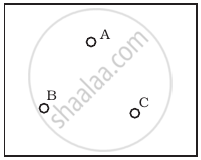 (a) |
Three components namely, two germanium diodes and one resistor are connected across these three terminals in some arrangement. A student performs an experiment in which any two of these three terminals are connected in the circuit shown in figure (b).
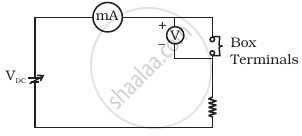 (b) |
The student obtains graphs of current-voltage characteristics for unknown combination of components between the two terminals connected in the circuit. The graphs are
(i) when A is positive and B is negative
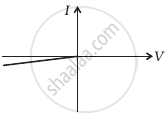 (c) |
(ii) when A is negative and B is positive
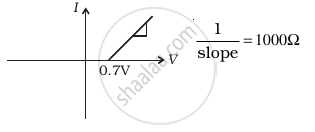 (d) |
(iii) When B is negative and C is positive
|
(e) |
(iv) When B is positive and C is negative
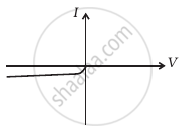 (f) |
(v) When A is positive and C is negative
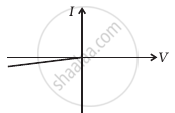 (g) |
(vi) When A is negative and C is positive
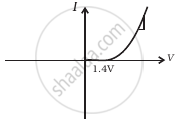 (h) |
From these graphs of current-voltage characteristics shown in figure (c) to (h), determine the arrangement of components between A, B and C.
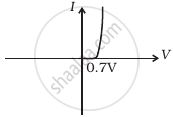
Draw a labelled characteristic curve (l-V graph) for a semiconductor diode during forward bias.