Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
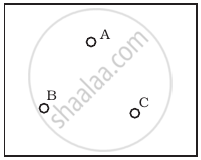
Consider a box with three terminals on top of it as shown in figure (a):
 (a) |
Three components namely, two germanium diodes and one resistor are connected across these three terminals in some arrangement. A student performs an experiment in which any two of these three terminals are connected in the circuit shown in figure (b).
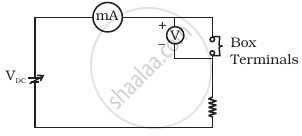 (b) |
The student obtains graphs of current-voltage characteristics for unknown combination of components between the two terminals connected in the circuit. The graphs are
(i) when A is positive and B is negative
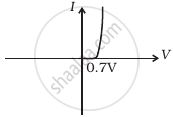
 (c) |
(ii) when A is negative and B is positive
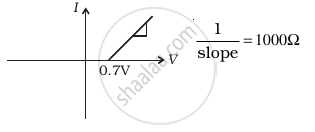 (d) |
(iii) When B is negative and C is positive
|
(e) |
(iv) When B is positive and C is negative
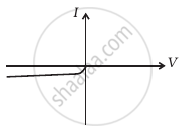 (f) |
(v) When A is positive and C is negative
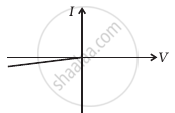 (g) |
(vi) When A is negative and C is positive
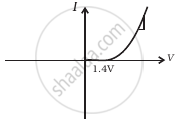 (h) |
From these graphs of current-voltage characteristics shown in figure (c) to (h), determine the arrangement of components between A, B and C.
उत्तर
The V-I characteristics of these graphs are discussed in points:
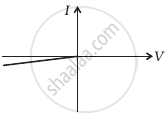
(a) In the V-I graph of condition (i), reverse characteristics are shown in figure (c). Here A is connected to the n-side of p-n junction I and B is connected top-side of the p-n junction I with a resistance in series.
(b) In the V-I graph of condition (ii), a forward characteristic is shown in figure (d), where 0.7 V is the knee voltage of p-n junction I. 1/slope = (1/1000) Ω.
It means A is connected to the n-side of p-n junction I and B is connected to the p-side of p-n junction I and resistance R is in a series of p-n junction I between A and B.
(c) In the V-I graph of condition (iii), a forward characteristic is shown in figure (e), where 0.7 V is the knee voltage. In this case, p-side of p-n junction II is connected to C and the n-side of p-n junction II to B.
(d) In V-I graphs of conditions (iv), (v), (vi) also concludes the above connection of p-n junctions I and II along with a resistance R.
Thus, the arrangement of p-n I, p-n II and resistance R between A, B and C will be as shown in the figure.
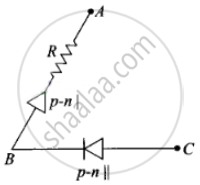
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw a labelled diagram of a full wave rectifier. Show how output voltage varies with time if the input voltage is a sinusoidal voltage.
The plate current in a diode is 20 mA when the plate voltage is 50 V or 60 V. What will be the current if the plate voltage is 70 V?
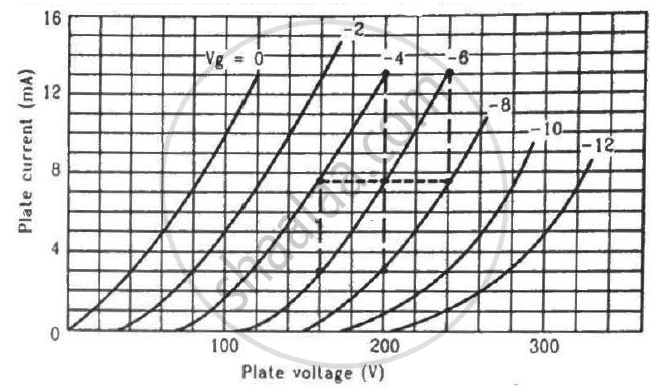
Find the values of rp, µ and gm of a triode operating at plate voltage 200 V and grid voltage −6. The plate characteristics are shown in the figure.
Of the diodes shown in the following diagrams, which one is reverse biased?
In forward bias width of potential barrier in a p + n junction diode
Use a transistor as an amplition
In a semiconductor diode, the barrier potential offers opposition to only
Consider an npn transistor with its base-emitter junction forward biased and collector base junction reverse biased. Which of the following statements are true?
- Electrons crossover from emitter to collector.
- Holes move from base to collector.
- Electrons move from emitter to base.
- Electrons from emitter move out of base without going to the collector.
Figure shows the transfer characteristics of a base biased CE transistor. Which of the following statements are true?

At Vi = 0.4 V, transistor is in active state.
At Vi = 1 V, it can be used as an amplifier.
At Vi = 0.5 V, it can be used as a switch turned off.
At Vi = 2.5 V, it can be used as a switch turned on.
With reference to a semiconductor diode, define the depletion region.