Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
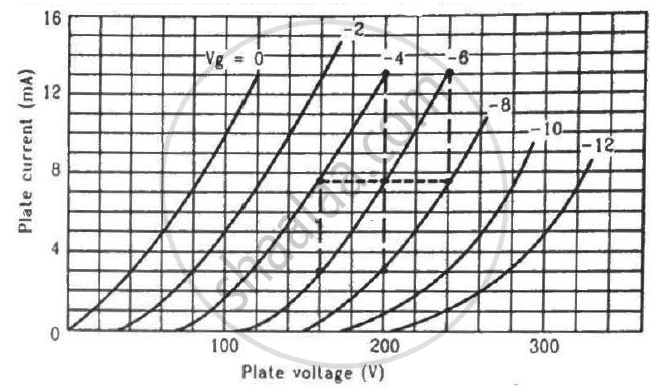
Find the values of rp, µ and gm of a triode operating at plate voltage 200 V and grid voltage −6. The plate characteristics are shown in the figure.
उत्तर
Dynamic plate resistance, `r_p=((deltaV_p)/(deltaI_p)),` at constant grid voltage
We need to find the slope of the graph for a particular value of grid voltage, i.e. Vg = −6 V.
Consider two points for the plot of Vg = −6 V:-
\[r_p = \frac{(240 - 160) V}{(13 - 3) \times {10}^{- 3} A}\]
\[ r_p = \frac{80}{10} \times {10}^3 \Omega\]
\[ r_p = 8 K\Omega\]
\[ g_m = \left( \frac{\delta I_p}{\delta V_g} \right)_{V_P = \text{constant } (200 V)}\]
Consider two points on the 200 V line:-
\[g_m = \frac{(13 - 3) \times {10}^{- 3}}{[( - 4) - ( - 8)]}A\]
\[ g_m = \frac{10 \times {10}^{- 3}}{4}=2.5\text{ mili mho}\]
Amplification factor,
\[\mu = - \left( \frac{∆ V_P}{∆ V_G} \right)_{i_P =\text{ constant}}\]
\[\mu = - \frac{100 - 180}{- 6 - ( - 10)}\]
\[\mu = \frac{80}{4} = 20\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
(i) Explain with the help of a diagram the formation of depletion region and barrier potential in a pn junction.
What happens when a forward bias is applied to a p-n junction?
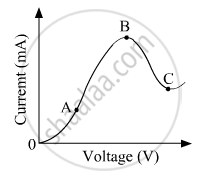
The graph shown in the figure represents a plot of current versus voltage for a given semiconductor. Identify the region, if any, over which the semiconductor has a negative resistance.
With reference to a semiconductor diode, what is meant by:
(i) Forward bias
(ii) Reverse bias
(iii) Depletion region
Answer the following question.
Why photodiodes are required to operate in reverse bias? Explain.
We use alloys for making standard resistors because they have ____________.
With reference to Semiconductor Physics,
Name the diode that emits spontaneous radiation when forward biased.
When an electric field is applied across a semiconductor ______.
- electrons move from lower energy level to higher energy level in the conduction band.
- electrons move from higher energy level to lower energy level in the conduction band.
- holes in the valence band move from higher energy level to lower energy level.
- holes in the valence band move from lower energy level to higher energy level.
In the depletion region of a diode ______.
- there are no mobile charges.
- equal number of holes and electrons exist, making the region neutral.
- recombination of holes and electrons has taken place.
- immobile charged ions exist.
The breakdown in a reverse biased p–n junction diode is more likely to occur due to ______.
- large velocity of the minority charge carriers if the doping concentration is small.
- large velocity of the minority charge carriers if the doping concentration is large.
- strong electric field in a depletion region if the doping concentration is small.
- strong electric field in the depletion region if the doping concentration is large.
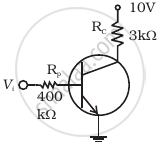
In the circuit shown in figure, when the input voltage of the base resistance is 10 V, Vbe is zero and Vce is also zero. Find the values of Ib, Ic and β.
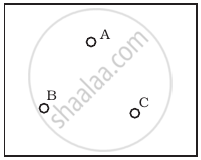
Consider a box with three terminals on top of it as shown in figure (a):
 (a) |
Three components namely, two germanium diodes and one resistor are connected across these three terminals in some arrangement. A student performs an experiment in which any two of these three terminals are connected in the circuit shown in figure (b).
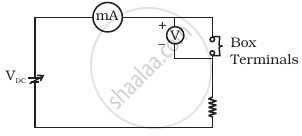 (b) |
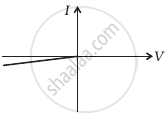
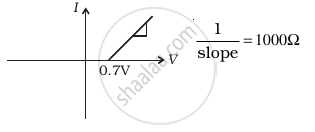
The student obtains graphs of current-voltage characteristics for unknown combination of components between the two terminals connected in the circuit. The graphs are
(i) when A is positive and B is negative
 (c) |
(ii) when A is negative and B is positive
 (d) |
(iii) When B is negative and C is positive
|
(e) |
(iv) When B is positive and C is negative
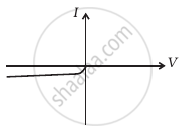 (f) |
(v) When A is positive and C is negative
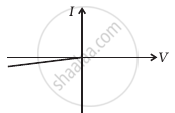 (g) |
(vi) When A is negative and C is positive
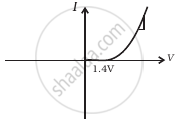 (h) |
From these graphs of current-voltage characteristics shown in figure (c) to (h), determine the arrangement of components between A, B and C.
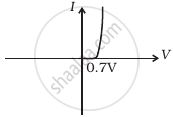
Draw V-I characteristics of a p-n Junction diode.
Answer the following giving reasons:
A p-n junction diode is damaged by a strong current.
Describe briefly the following term:
breakdown voltage in reverse biasing
With reference to a semiconductor diode, define the potential barrier.
Draw a labelled characteristic curve (l-V graph) for a semiconductor diode during forward bias.