Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Find the values of rp, µ and gm of a triode operating at plate voltage 200 V and grid voltage −6. The plate characteristics are shown in the figure.
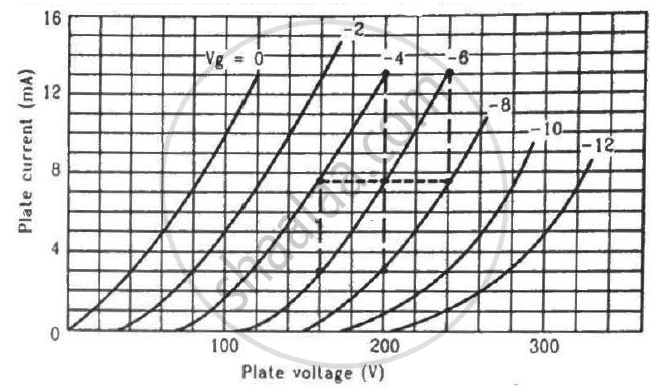
उत्तर
Dynamic plate resistance, `r_p=((deltaV_p)/(deltaI_p)),` at constant grid voltage
We need to find the slope of the graph for a particular value of grid voltage, i.e. Vg = −6 V.
Consider two points for the plot of Vg = −6 V:-
\[r_p = \frac{(240 - 160) V}{(13 - 3) \times {10}^{- 3} A}\]
\[ r_p = \frac{80}{10} \times {10}^3 \Omega\]
\[ r_p = 8 K\Omega\]
\[ g_m = \left( \frac{\delta I_p}{\delta V_g} \right)_{V_P = \text{constant } (200 V)}\]
Consider two points on the 200 V line:-
\[g_m = \frac{(13 - 3) \times {10}^{- 3}}{[( - 4) - ( - 8)]}A\]
\[ g_m = \frac{10 \times {10}^{- 3}}{4}=2.5\text{ mili mho}\]
Amplification factor,
\[\mu = - \left( \frac{∆ V_P}{∆ V_G} \right)_{i_P =\text{ constant}}\]
\[\mu = - \frac{100 - 180}{- 6 - ( - 10)}\]
\[\mu = \frac{80}{4} = 20\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
With the help of neat labelled circuit diagram explain the working of half wave rectifier using semiconductor diode. Draw the input and output waveforms.
When a forward bias is applied to a p-n junction, it ______.
Draw a labelled diagram of a full wave rectifier. Show how output voltage varies with time if the input voltage is a sinusoidal voltage.
With reference to a semiconductor diode, what is meant by:
(i) Forward bias
(ii) Reverse bias
(iii) Depletion region
Answer the following question.
Why photodiodes are required to operate in reverse bias? Explain.
Basic materials used in the present solid state electronic devices like diode, transistor, ICs, etc are ______.
A – pn junction has a depletion layer of thickness .of the order of
Use a transistor as an amplition
On increasing the reverse biases voltage to a large value in a P – N junction diode-current
When an electric field is applied across a semiconductor ______.
- electrons move from lower energy level to higher energy level in the conduction band.
- electrons move from higher energy level to lower energy level in the conduction band.
- holes in the valence band move from higher energy level to lower energy level.
- holes in the valence band move from lower energy level to higher energy level.
Consider an npn transistor with its base-emitter junction forward biased and collector base junction reverse biased. Which of the following statements are true?
- Electrons crossover from emitter to collector.
- Holes move from base to collector.
- Electrons move from emitter to base.
- Electrons from emitter move out of base without going to the collector.
Consider an npn transistor with its base-emitter junction forward biased and collector base junction reverse biased. Which of the following statements are true?
- Electrons crossover from emitter to collector.
- Holes move from base to collector.
- Electrons move from emitter to base.
- Electrons from emitter move out of base without going to the collector.
In the depletion region of a diode ______.
- there are no mobile charges.
- equal number of holes and electrons exist, making the region neutral.
- recombination of holes and electrons has taken place.
- immobile charged ions exist.
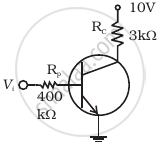
In the circuit shown in figure, when the input voltage of the base resistance is 10 V, Vbe is zero and Vce is also zero. Find the values of Ib, Ic and β.
Write the property of a junction diode which makes it suitable for rectification of ac voltages.
Answer the following giving reasons:
A p-n junction diode is damaged by a strong current.
Describe briefly the following term:
minority carrier injection in forward biasing.
Read the following paragraph and answer the questions that follow.
| A semiconductor diode is basically a pn junction with metallic contacts provided at the ends for the application of an external voltage. It is a two-terminal device. When an external voltage is applied across a semiconductor diode such that the p-side is connected to the positive terminal of the battery and the n-side to the negative terminal, it is said to be forward-biased. When an external voltage is applied across the diode such that the n-side is positive and the p-side is negative, it is said to be reverse-biased. An ideal diode is one whose resistance in forward biasing is zero and the resistance is infinite in reverse biasing. When the diode is forward biased, it is found that beyond forward voltage called knee voltage, the conductivity is very high. When the biasing voltage is more than the knee voltage the potential barrier is overcome and the current increases rapidly with an increase in forward voltage. When the diode is reverse biased, the reverse bias voltage produces a very small current of about a few microamperes which almost remains constant with bias. This small current is a reverse saturation current. |
- In the given figure, a diode D is connected to an external resistance R = 100 Ω and an emf of 3.5 V. If the barrier potential developed across the diode is 0.5 V, the current in the circuit will be:

(a) 40 mA
(b) 20 mA
(c) 35 mA
(d) 30 mA - In which of the following figures, the pn diode is reverse biased?
(a)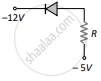
(b)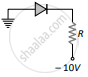
(c)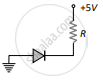
(d)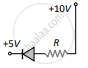
- Based on the V-I characteristics of the diode, we can classify the diode as:
(a) bilateral device
(b) ohmic device
(c) non-ohmic device
(d) passive element
OR
Two identical PN junctions can be connected in series by three different methods as shown in the figure. If the potential difference in the junctions is the same, then the correct connections will be:
(a) in the circuits (1) and (2)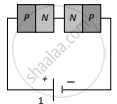
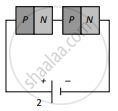
(b) in the circuits (2) and (3)
(c) in the circuits (1) and (3)
(d) only in the circuit (1) 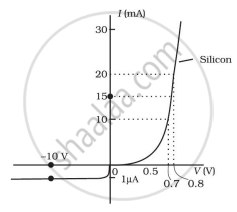
The V-I characteristic of a diode is shown in the figure. The ratio of the resistance of the diode at I = 15 mA to the resistance at V = -10 V is
(a) 100
(b) 106
(c) 10
(d) 10-6
An ideal PN junction diode offers ______.
