Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Write the property of a junction diode which makes it suitable for rectification of ac voltages.
Which characteristic property makes the junction diode suitable for rectification?
State the characteristic property of a junction diode that makes it suitable for rectification.
उत्तर
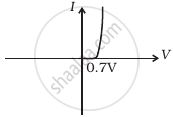
When a junction diode has an alternating voltage placed across it, only when the diode is forward-biased can current flow. The junction diode's ability to correct alternating current can be used. This is accomplished through the use of a rectifier circuit. It exhibits high resistance when reverse-biased and low resistance when forward-biased.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In the following diagram, is the junction diode forward biased or reverse biased ?
In semiconductor physics, what is meant by:
(i) rectifier
(ii) an amplifier
(iii) an oscillator
Basic materials used in the present solid state electronic devices like diode, transistor, ICs, etc are ______.
Diffusion in a p-n junction is due to ______.
What are the applications of p - n Junction diode?
Depletion layer in p - n junction diode consists of
In a semiconductor diode, the barrier potential offers opposition to only
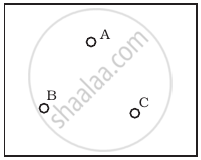
Consider a box with three terminals on top of it as shown in figure (a):
 (a) |
Three components namely, two germanium diodes and one resistor are connected across these three terminals in some arrangement. A student performs an experiment in which any two of these three terminals are connected in the circuit shown in figure (b).
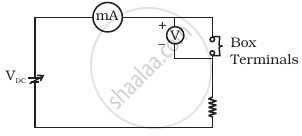 (b) |
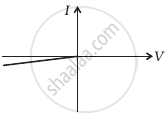
The student obtains graphs of current-voltage characteristics for unknown combination of components between the two terminals connected in the circuit. The graphs are
(i) when A is positive and B is negative
 (c) |
(ii) when A is negative and B is positive
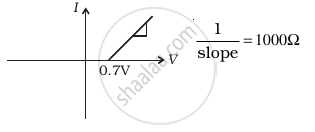 (d) |
(iii) When B is negative and C is positive
|
(e) |
(iv) When B is positive and C is negative
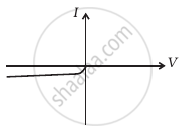 (f) |
(v) When A is positive and C is negative
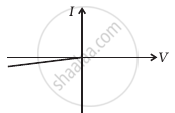 (g) |
(vi) When A is negative and C is positive
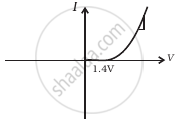 (h) |
From these graphs of current-voltage characteristics shown in figure (c) to (h), determine the arrangement of components between A, B and C.
Draw the circuit arrangement for studying V-I characteristics of a p-n junction diode in (i) forward biasing and (ii) reverse biasing. Draw the typical V-I characteristics of a silicon diode.
Draw a labelled characteristic curve (l-V graph) for a semiconductor diode during forward bias.