Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Draw the circuit arrangement for studying V-I characteristics of a p-n junction diode in (i) forward biasing and (ii) reverse biasing. Draw the typical V-I characteristics of a silicon diode.
उत्तर
Forward biasing:
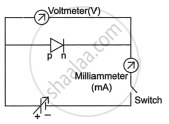
Fig. (a)
Reverse biasing:
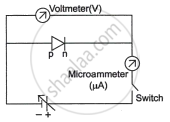
Fig. (b)

Fig. (c)
Figures (a) and (b) depict the circuit for examining a diode's V-I properties. The value of current is noted for various voltage values. The result is a graph between C and I, as shown in Fig. (c).
It is evident from a junction diode's V-I characteristics that current can only flow through it when it is forward biassed. As a result, when alternating voltage is placed across a forward biassed diode, current only flows during a portion of the cycle. Alternating voltages are rectified using this characteristic.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw a labelled diagram of a full wave rectifier. Show how output voltage varies with time if the input voltage is a sinusoidal voltage.
With reference to semi-conductors answer the following :
(i) What is the change in the resistance of the semi-conductor with increase in temperature ?
(ii) Name the majority charge carriers in n-type semi-conductor.
(iii) What is meant by doping ?
The plate current in a diode is 20 mA when the plate voltage is 50 V or 60 V. What will be the current if the plate voltage is 70 V?
Basic materials used in the present solid state electronic devices like diode, transistor, ICs, etc are ______.
We use alloys for making standard resistors because they have ____________.
The drift current in a p-n junction is from the ______.
The breakdown in a reverse biased p–n junction diode is more likely to occur due to ______.
- large velocity of the minority charge carriers if the doping concentration is small.
- large velocity of the minority charge carriers if the doping concentration is large.
- strong electric field in a depletion region if the doping concentration is small.
- strong electric field in the depletion region if the doping concentration is large.
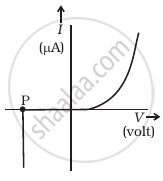 (a) |
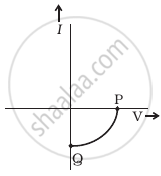 (b) |
- Name the type of a diode whose characteristics are shown in figure (A) and figure (B).
- What does the point P in figure (A) represent?
- What does the points P and Q in figure (B) represent?
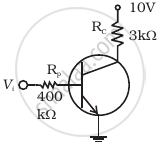
In the circuit shown in figure, when the input voltage of the base resistance is 10 V, Vbe is zero and Vce is also zero. Find the values of Ib, Ic and β.
What is meant by forward biasing of a semiconductor diode?
