Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Write the two processes that take place in the formation of a p-n junction.
Name two important processes involved in the formation of a p-n junction diode.
उत्तर
The processes of "diffusion" and "drift" are critical in a p-n junction. When the p and n-sides come into contact, the majority of carriers "diffuse" from a high concentration to a low concentration. Electrons move and combine with holes from the n-side to the p-side. Holes migrate from the p-side to the n-side in the same way that electrons and holes do at the junction. A "depletion region" is formed when the near junction area runs out of carriers and becomes charged. Current "diffusion" is caused by current "diffusion."
In the depletion area, the charge produces an electric field. The electric field creates a flow of minority carriers in the 'depletion' region. The produced current is known as "drift current," and it is referred to as drift. The directions of "diffusion and drift current" are reversed.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A student wants to use two p-n junction diodes to convert alternating current into direct current. Draw the labelled circuit diagram she would use and explain how it works.
Explain, with the help of a circuit diagram, the working of a photo-diode. Write briefly how it is used to detect the optical signals.
Diffusion current in a p-n junction is greater than the drift current in magnitude
A hole diffuses from the p-side to the n-side in a p-n junction. This means that
In a p-n junction with open ends,
(a) there is no systematic motion of charge carries
(b) holes and conduction electrons systematically go from the p-side to n-side and from the n-side to p-side respectively
(c) there is no net charge transfer between the two sides
(d) there is a constant electric field near the junction.
A semiconducting device is connected in a series circuit with a battery and a resistance. A current is found to pass through the circuit. If the polarity of the battery is reversed, the current drops to almost zero. the device may be
(a) an intrinsic semiconductor
(b) a p-type semiconductor
(c) an n-type semiconductor
(d) a p-n junction
Find the current through the resistance R in figure if (a) R = 12Ω (b) R = 48Ω.
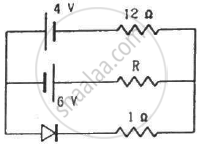
(Assume that the resistance of each diode is zero in forward bias and is infinity in reverse bias.)
Find the equivalent resistance of the network shown in figure between the points A and B.
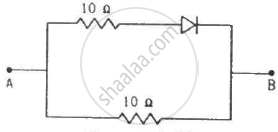
(Assume that the resistance of each diode is zero in forward bias and is infinity in reverse bias.)
When the base current in a transistor is changed from 30µA to 80µA, the collector current is changed from 1.0 mA to 3.5 mA. Find the current gain β.
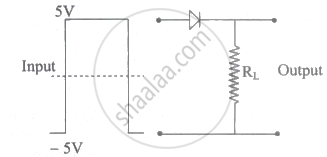
If in a p-n junction diode, a square input signal of 10 V is applied as shown Then the output signal across RL will be ______