Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
When the base current in a transistor is changed from 30µA to 80µA, the collector current is changed from 1.0 mA to 3.5 mA. Find the current gain β.
उत्तर
Given:
Change in the base current, \[\delta I_b = (80 - 30) \mu \text{A}\]
Change in the collector current, \[\delta I_c = (3 . 5 - 1) \] mA
Thus,
\[\beta = \left( \frac{\delta l_c}{\delta l_b} \right) \text{at constant V}_{cc} \]
\[ \Rightarrow \beta = \frac{2 . 5 \times {10}^{- 3}}{50 \times {10}^{- 6}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \beta = \frac{250}{50} = 50\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In an unbiased p-n junction, holes diffuse from the p-region to n-region because ______.
A zener diode is fabricated by heavily doping both p- and n- sides of the junction. Explain, why?
Explain briefly with the help of necessary diagrams, the reverse biasing of a p-n junction diode. Also draw characteristic curves.
The drift current in a reverse-biased p-n junction is increased in magnitude if the temperature of the junction is increased. Explain this on the basis of creation of hole-electron pairs.
The diffusion current in a p-n junction is
Diffusion current in a p-n junction is greater than the drift current in magnitude
A hole diffuses from the p-side to the n-side in a p-n junction. This means that
In a p-n junction with open ends,
(a) there is no systematic motion of charge carries
(b) holes and conduction electrons systematically go from the p-side to n-side and from the n-side to p-side respectively
(c) there is no net charge transfer between the two sides
(d) there is a constant electric field near the junction.
The current−voltage characteristic of an ideal p-n junction diode is given by \[i = i_0 ( e^{eV/KT} - 1)\] where, the drift current i0 equals 10 µA. Take the temperature T to be 300 K. (a) Find the voltage V0 for which \[e^{eV/kT} = 100 .\]One can neglect the term 1 for voltages greater than this value. (b) Find an expression for the dynamic resistance of the diode as a function of V for V > V0. (c) Find the voltage for which the dynamic resistance is 0.2 Ω.
(Use Planck constant h = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, Boltzmann constant k = 8·62 × 10-5 eV/K.)
Find the currents through the resistance in the circuits shown in figure.
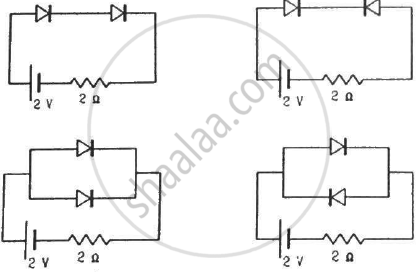
(Assume that the resistance of each diode is zero in forward bias and is infinity in reverse bias.)
What are the readings of the ammeters A1 and A2 shown in figure. Neglect the resistance of the meters.
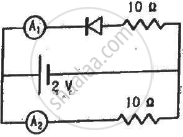
(Assume that the resistance of each diode is zero in forward bias and is infinity in reverse bias.)
Find the current through the resistance R in figure if (a) R = 12Ω (b) R = 48Ω.
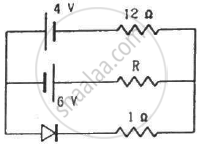
(Assume that the resistance of each diode is zero in forward bias and is infinity in reverse bias.)
Draw the current-voltage characteristics for the device show in figure between the terminals A and B.
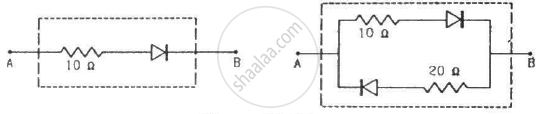
(Assume that the resistance of each diode is zero in forward bias and is infinity in reverse bias.)
Answer in detail.
Discuss the effect of external voltage on the width of depletion region of a p-n junction.
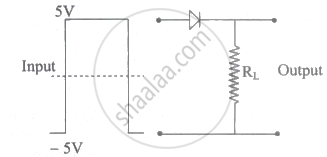
If in a p-n junction diode, a square input signal of 10 V is applied as shown Then the output signal across RL will be ______
The formation of the depletion region in a p-n junction diode is due to ______.
During the formation of a p-n junction ______.
