Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Write the two processes that take place in the formation of a p-n junction.
Name two important processes involved in the formation of a p-n junction diode.
उत्तर
The processes of "diffusion" and "drift" are critical in a p-n junction. When the p and n-sides come into contact, the majority of carriers "diffuse" from a high concentration to a low concentration. Electrons move and combine with holes from the n-side to the p-side. Holes migrate from the p-side to the n-side in the same way that electrons and holes do at the junction. A "depletion region" is formed when the near junction area runs out of carriers and becomes charged. Current "diffusion" is caused by current "diffusion."
In the depletion area, the charge produces an electric field. The electric field creates a flow of minority carriers in the 'depletion' region. The produced current is known as "drift current," and it is referred to as drift. The directions of "diffusion and drift current" are reversed.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A zener diode is fabricated by heavily doping both p- and n- sides of the junction. Explain, why?
Explain, with the help of a circuit diagram, the working of a photo-diode. Write briefly how it is used to detect the optical signals.
Draw a circuit diagram to study the input and output characteristics of an n-p-n transistor in its common emitter configuration. Draw the typical input and output characteristics.
If the two ends of a p-n junction are joined by a wire,
The potential barrier existing across an unbiased p-n junction is 0.2 volt. What minimum kinetic energy a hole should have to diffuse from the p-side to the n-side if (a) the junction is unbiased, (b) the junction is forward-biased at 0.1 volt and (c) the junction is reverse-biased at 0.1 volt?
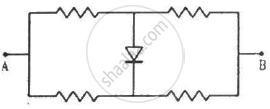
Each of the resistance shown in figure has a value of 20 Ω. Find the equivalent resistance between A and B. Does it depend on whether the point A or B is at higher potential?
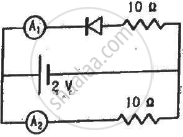
What are the readings of the ammeters A1 and A2 shown in figure. Neglect the resistance of the meters.
(Assume that the resistance of each diode is zero in forward bias and is infinity in reverse bias.)
Find the current through the battery in each of the circuits shown in figure.
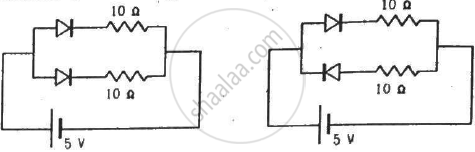
(Assume that the resistance of each diode is zero in forward bias and is infinity in reverse bias.)
Find the current through the resistance R in figure if (a) R = 12Ω (b) R = 48Ω.
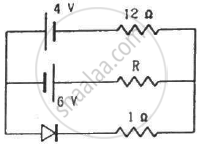
(Assume that the resistance of each diode is zero in forward bias and is infinity in reverse bias.)
A load resistor of 2kΩ is connected in the collector branch of an amplifier circuit using a transistor in common-emitter mode. The current gain β = 50. The input resistance of the transistor is 0.50 kΩ. If the input current is changed by 50µA. (a) by what amount does the output voltage change, (b) by what amount does the input voltage change and (c) what is the power gain?
