Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Each of the resistance shown in figure has a value of 20 Ω. Find the equivalent resistance between A and B. Does it depend on whether the point A or B is at higher potential?
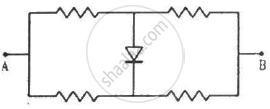
उत्तर
According to the Wheatstone bridge principle, if the bridge is balanced, then the current flow across the central resistor is zero. So, to simplify the circuit, we can remove the central resistor.
The given circuit is also balanced, so there is no current through the diode.
Hence, the net resistance of the circuit is given by
\[R_P = \frac{R_1 R_2}{R_1 + R_2}\]
\[\text{For } R_1 = R_2 = R, \]
\[ R_P = \frac{R}{2} = \frac{40}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow R_P = 20 \Omega\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In an unbiased p-n junction, holes diffuse from the p-region to n-region because ______.
A zener diode is fabricated by heavily doping both p- and n- sides of the junction. Explain, why?
Explain briefly with the help of necessary diagrams, the reverse biasing of a p-n junction diode. Also draw characteristic curves.
When a p-type impurity is doped in a semiconductor, a large number of holes are created, This does not make the semiconductor charged. But when holes diffuse from the p-side to the n-side in a p-n junction, the n-side gets positively charged. Explain.
If the two ends of a p-n junction are joined by a wire,
The drift current in a p-n junction is
Two identical p-n junction may be connected in series with a battery in three ways. The potential difference across the two p-n junctions are equal in
In a p.n junction, the depletion region is 400 nm wide and an electric field of 5 × 105 V m−1 exists in it. (a) Find the height of the potential barrier. (b) What should be the minimum kinetic energy of a conduction electron which can diffuse from the n-side to the p-side?
The potential barrier existing across an unbiased p-n junction is 0.2 volt. What minimum kinetic energy a hole should have to diffuse from the p-side to the n-side if (a) the junction is unbiased, (b) the junction is forward-biased at 0.1 volt and (c) the junction is reverse-biased at 0.1 volt?
In a p-n junction, a potential barrier of 250 meV exists across the junction. A hole with a kinetic energy of 300 meV approaches the junction. Find the kinetic energy of the hole when it crosses the junction if the hole approached the junction (a) from the p-side and (b) from the n-side.
When a p-n junction is reverse-biased, the current becomes almost constant at 25 µA. When it is forward-biased at 200 mV, a current of 75 µA is obtained. Find the magnitude of diffusion current when the diode is
(a) unbiased,
(b) reverse-biased at 200 mV and
(c) forward-biased at 200 mV.
Consider a p-n junction diode having the characteristic \[i - i_0 ( e^{eV/kT} - 1) \text{ where } i_0 = 20\mu A\] . The diode is operated at T = 300 K . (a) Find the current through the diode when a voltage of 300 mV is applied across it in forward bias. (b) At what voltage does the current double?
Find the currents through the resistance in the circuits shown in figure.
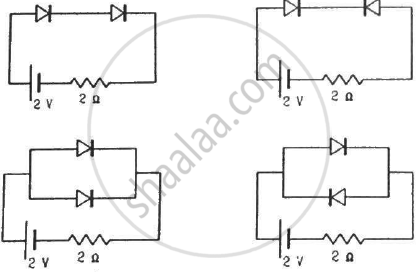
(Assume that the resistance of each diode is zero in forward bias and is infinity in reverse bias.)
Draw the current-voltage characteristics for the device show in figure between the terminals A and B.
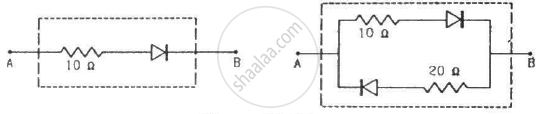
(Assume that the resistance of each diode is zero in forward bias and is infinity in reverse bias.)
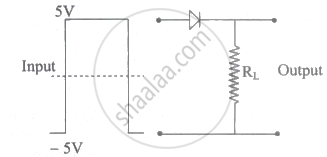
If in a p-n junction diode, a square input signal of 10 V is applied as shown Then the output signal across RL will be ______
p-n junction diode is formed
Zener breakdown occurs in a p-n junction having p and n both:
The formation of the depletion region in a p-n junction diode is due to ______.
During the formation of a p-n junction ______.
