Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
When a p-type impurity is doped in a semiconductor, a large number of holes are created, This does not make the semiconductor charged. But when holes diffuse from the p-side to the n-side in a p-n junction, the n-side gets positively charged. Explain.
उत्तर
A p-type semiconductor is formed by doping a group 13 element with group 14 element (Si or Ge). As the group 13 element has only 3 electrons in its valence shell and the group 14 element has 4 electrons in its valence shell, when the group 13 element, say, Al, replaces one Si in the silicon crystal, only 3 covalent bonds are formed by it. And the fourth covalent bond is left in need of one electron. So, it creates a hole. Since the atom as a whole is electriclly neutral, the p-type semiconductor is also neutral.
In a p‒n junction, when the diffusion of holes takes place across the junction because of the difference in the concentration of charge carriers from p to n sides, these holes neutralise some of the electrons on the n side. So, the atom attached with that electron becomes one electron deficient and hence positively charged. This makes the n side of the p‒n junction positively charged and the p side of the p‒n junction negatively charged.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain briefly with the help of necessary diagrams, the reverse biasing of a p-n junction diode. Also draw characteristic curves.
Explain, with the help of a circuit diagram, the working of a photo-diode. Write briefly how it is used to detect the optical signals.
Mention the important considerations required while fabricating a p-n junction diode to be used as a Light Emitting Diode (LED). What should be the order of band gap of an LED if it is required to emit light in the visible range?
Explain, with the help of a circuit diagram, the working of n-p-n transistor as a common emitter amplifier.
If the two ends of a p-n junction are joined by a wire,
The diffusion current in a p-n junction is
Diffusion current in a p-n junction is greater than the drift current in magnitude
Two identical p-n junction may be connected in series with a battery in three ways. The potential difference across the two p-n junctions are equal in
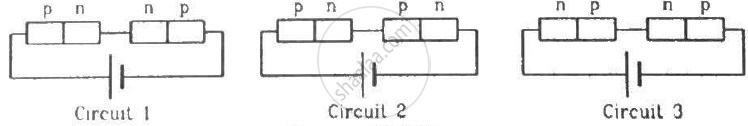
In a p-n junction with open ends,
(a) there is no systematic motion of charge carries
(b) holes and conduction electrons systematically go from the p-side to n-side and from the n-side to p-side respectively
(c) there is no net charge transfer between the two sides
(d) there is a constant electric field near the junction.
When a p-n junction is reverse-biased, the current becomes almost constant at 25 µA. When it is forward-biased at 200 mV, a current of 75 µA is obtained. Find the magnitude of diffusion current when the diode is
(a) unbiased,
(b) reverse-biased at 200 mV and
(c) forward-biased at 200 mV.
The drift current in a p-n junction is 20.0 µA. Estimate the number of electrons crossing a cross section per second in the depletion region.
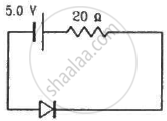
Calculate the current through the circuit and the potential difference across the diode shown in figure. The drift current for the diode is 20 µA.
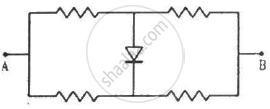
Each of the resistance shown in figure has a value of 20 Ω. Find the equivalent resistance between A and B. Does it depend on whether the point A or B is at higher potential?
Find the current through the battery in each of the circuits shown in figure.
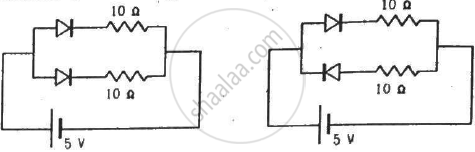
(Assume that the resistance of each diode is zero in forward bias and is infinity in reverse bias.)
Draw the current-voltage characteristics for the device show in figure between the terminals A and B.
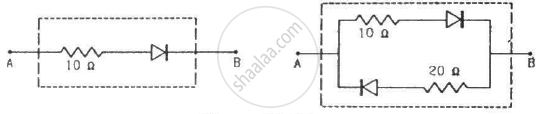
(Assume that the resistance of each diode is zero in forward bias and is infinity in reverse bias.)
When the base current in a transistor is changed from 30µA to 80µA, the collector current is changed from 1.0 mA to 3.5 mA. Find the current gain β.
An AC source is connected to a diode and a resistor in series. Is the current thorough the resistor AC or DC?
Choose the correct option.
Current through a reverse-biased p-n junction increases abruptly at:
p-n junction diode is formed
During the formation of a p-n junction ______.
