Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
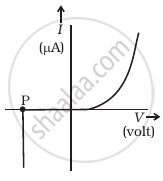 (a) |
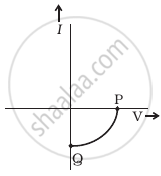 (b) |
- Name the type of a diode whose characteristics are shown in figure (A) and figure (B).
- What does the point P in figure (A) represent?
- What does the points P and Q in figure (B) represent?
उत्तर
- Figure (a) represents the characteristics of the Zener diode and curve (b) is of the solar cell.
- In figure (a), point P represents Zener breakdown voltage.
- In figure (b), point Q represents zero voltage and negative current. This means the light falling on the solar cell with at least a minimum threshold frequency gives the current in opposite direction to that due to a battery connected to solar cell. But for point Q the battery is short-circuited. Hence it represents the short circuit current. And the point Pin fig. (b) represents some open circuit, the voltage on solar cell with zero current through solar cell.
It means, there is a battery connected to a solar cell which gives rise to the equal and opposite current to that in a solar cell by virtue of light falling on it.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw a labelled diagram of a full wave rectifier. Show how output voltage varies with time if the input voltage is a sinusoidal voltage.
In semiconductor physics, what is meant by:
(i) rectifier
(ii) an amplifier
(iii) an oscillator
Basic materials used in the present solid state electronic devices like diode, transistor, ICs, etc are ______.
When we apply reverse biased to a junction diode, it
Consider an npn transistor with its base-emitter junction forward biased and collector base junction reverse biased. Which of the following statements are true?
- Electrons crossover from emitter to collector.
- Holes move from base to collector.
- Electrons move from emitter to base.
- Electrons from emitter move out of base without going to the collector.
Figure shows the transfer characteristics of a base biased CE transistor. Which of the following statements are true?

At Vi = 0.4 V, transistor is in active state.
At Vi = 1 V, it can be used as an amplifier.
At Vi = 0.5 V, it can be used as a switch turned off.
At Vi = 2.5 V, it can be used as a switch turned on.
Write the property of a junction diode which makes it suitable for rectification of ac voltages.
Describe briefly the following term:
minority carrier injection in forward biasing.
With reference to a semiconductor diode, define the potential barrier.
What is meant by forward biasing of a semiconductor diode?
