Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Figure shows the transfer characteristics of a base biased CE transistor. Which of the following statements are true?

At Vi = 0.4 V, transistor is in active state.
At Vi = 1 V, it can be used as an amplifier.
At Vi = 0.5 V, it can be used as a switch turned off.
At Vi = 2.5 V, it can be used as a switch turned on.
पर्याय
a and c
a, c and d
b and c
b, c and d
उत्तर
b, c and d
Explanation:
According to the above graph transfer characteristics of a base biased common emitter transistor, we note that.
- When Vi= 0.4 V, the output voltage remain same and there is no collection current. So, the transistor circuit is not in an active state.
- When Vi = 1 V (This is in between 0.6 V to 2 V), the transistor circuit is in an active state and when input is increasing output is decreasing because when CE is used as an amplifier input and output voltages are 180° out of phase. Then it is used as an amplifier.
- When Vi = 0.5 V, there is no collector current. The transistor is in a cut-off state. The transistor circuit can be used as a switch to be turned off.
- When Vi = 2.5 V, the collector current becomes maximum and the transistor is in a saturation state and can be used as a switch turned on state.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
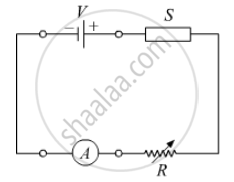
In the following diagram 'S' is a semiconductor. Would you increase or decrease the value of R to keep the reading of the ammeter A constant when S is heated? Give reason for your answer.
Draw a labelled diagram of a full wave rectifier. Show how output voltage varies with time if the input voltage is a sinusoidal voltage.
We use alloys for making standard resistors because they have ____________.
What are the applications of p - n Junction diode?
In a semiconductor diode, the barrier potential offers opposition to only
When an electric field is applied across a semiconductor ______.
- electrons move from lower energy level to higher energy level in the conduction band.
- electrons move from higher energy level to lower energy level in the conduction band.
- holes in the valence band move from higher energy level to lower energy level.
- holes in the valence band move from lower energy level to higher energy level.
Can the potential barrier across a p-n junction be measured by simply connecting a voltmeter across the junction?
The graph of potential barrier versus width of depletion region for an unbiased diode is shown in graph A. In comparison to A, graphs B and C are obtained after biasing the diode in different ways. Identify the type of biasing in B and C and justify your answer
| ‘A’ | ‘B’ | ‘C’ |
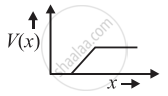 |
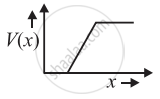 |
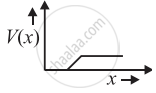 |
Draw the circuit arrangement for studying V-I characteristics of a p-n junction diode in (i) forward biasing and (ii) reverse biasing. Draw the typical V-I characteristics of a silicon diode.
What is meant by forward biasing of a semiconductor diode?
