Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
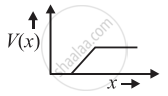
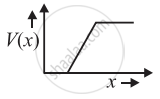
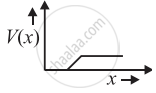
The graph of potential barrier versus width of depletion region for an unbiased diode is shown in graph A. In comparison to A, graphs B and C are obtained after biasing the diode in different ways. Identify the type of biasing in B and C and justify your answer
| ‘A’ | ‘B’ | ‘C’ |
 |
 |
 |
उत्तर
B - reverse biased
In the case of a reverse-biased diode, the potential barrier becomes higher as the battery further raises the potential of the n side.
C - forward biased
Due to the forward bias connection, the potential of P side is raised and hence the height of the potential barrier decreases.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What happens when a forward bias is applied to a p-n junction?
What causes the setting up of high electric field even for small reverse bias voltage across the diode?
The plate current in a diode is 20 mA when the plate voltage is 50 V or 60 V. What will be the current if the plate voltage is 70 V?
A triode value operates at Vp = 225 V and Vg = −0.5 V.
The plate current remains unchanged if the plate voltage is increased to 250 V and the grid voltage is decreased to −2.5 V. Calculate the amplification factor.
The gain factor of an amplifier in increased from 10 to 12 as the load resistance is changed from 4 kΩ to 8 kΩ. Calculate (a) the amplification factor and (b) the plate resistance.
Diffusion in a p-n junction is due to ______.
A – pn junction has a depletion layer of thickness .of the order of
When an electric field is applied across a semiconductor ______.
- electrons move from lower energy level to higher energy level in the conduction band.
- electrons move from higher energy level to lower energy level in the conduction band.
- holes in the valence band move from higher energy level to lower energy level.
- holes in the valence band move from lower energy level to higher energy level.
Figure shows the transfer characteristics of a base biased CE transistor. Which of the following statements are true?

At Vi = 0.4 V, transistor is in active state.
At Vi = 1 V, it can be used as an amplifier.
At Vi = 0.5 V, it can be used as a switch turned off.
At Vi = 2.5 V, it can be used as a switch turned on.
 (a) |
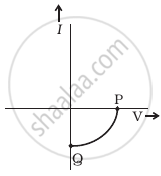 (b) |
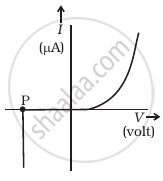
- Name the type of a diode whose characteristics are shown in figure (A) and figure (B).
- What does the point P in figure (A) represent?
- What does the points P and Q in figure (B) represent?
