Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What happens when a forward bias is applied to a p-n junction?
उत्तर
In forward biasing, the applied voltage mostly drops across the depletion region, and the voltage drop across the p-side and n-side of the junction is negligible. The direction of the applied voltage (V) is opposite to the built-in potential Vo. As a result, the depletion layer width decreases and the barrier height is reduced. The effective barrier height under forward bias is (Vo − V).
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A plate current of 10 mA is obtained when 60 volts are applied across a diode tube. Assuming the Langmuir-Child relation \[i_p \infty V_p^{3/2}\] to hold, find the dynamic resistance rp in this operating condition.
The plate current in a diode is 20 mA when the plate voltage is 50 V or 60 V. What will be the current if the plate voltage is 70 V?
A – pn junction has a depletion layer of thickness .of the order of
The expected energy of the electron at absolute zero is called:-
Consider an npn transistor with its base-emitter junction forward biased and collector base junction reverse biased. Which of the following statements are true?
- Electrons crossover from emitter to collector.
- Holes move from base to collector.
- Electrons move from emitter to base.
- Electrons from emitter move out of base without going to the collector.
The breakdown in a reverse biased p–n junction diode is more likely to occur due to ______.
- large velocity of the minority charge carriers if the doping concentration is small.
- large velocity of the minority charge carriers if the doping concentration is large.
- strong electric field in a depletion region if the doping concentration is small.
- strong electric field in the depletion region if the doping concentration is large.
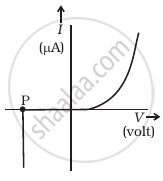 (a) |
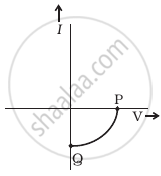 (b) |
- Name the type of a diode whose characteristics are shown in figure (A) and figure (B).
- What does the point P in figure (A) represent?
- What does the points P and Q in figure (B) represent?
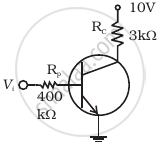
In the circuit shown in figure, when the input voltage of the base resistance is 10 V, Vbe is zero and Vce is also zero. Find the values of Ib, Ic and β.
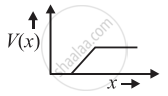
The graph of potential barrier versus width of depletion region for an unbiased diode is shown in graph A. In comparison to A, graphs B and C are obtained after biasing the diode in different ways. Identify the type of biasing in B and C and justify your answer
| ‘A’ | ‘B’ | ‘C’ |
 |
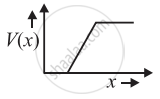 |
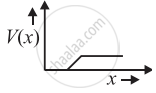 |
A semiconductor device is connected in series with a battery, an ammeter and a resistor. A current flows in the circuit. If. the polarity of the battery is reversed, the current in the circuit almost becomes zero. The device is a/an ______.
