Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A semiconductor device is connected in series with a battery, an ammeter and a resistor. A current flows in the circuit. If. the polarity of the battery is reversed, the current in the circuit almost becomes zero. The device is a/an ______.
पर्याय
intrinsic semiconductor
p-type semiconductor
n-type semiconductor
p-n junction diode
उत्तर
A semiconductor device is connected in series with a battery, an ammeter and a resistor. A current flows in the circuit. If. the polarity of the battery is reversed, the current in the circuit almost becomes zero. The device is a/an p-n junction diode.
Explanation:
When the battery's polarity is reversed, the p-n junction becomes reverse bias. As a result, its resistance rises and the current through the junction falls to nearly zero.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
(i) Explain with the help of a diagram the formation of depletion region and barrier potential in a pn junction.
With reference to semiconductor devices, define a p-type semiconductor and a Zener diode.
A triode value operates at Vp = 225 V and Vg = −0.5 V.
The plate current remains unchanged if the plate voltage is increased to 250 V and the grid voltage is decreased to −2.5 V. Calculate the amplification factor.
Diffusion in a p-n junction is due to ______.
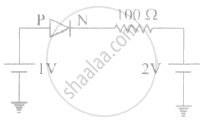
The current through an ideal PN-junction shown in the following circuit diagram will be:
Avalanche breakdown is due to ______.
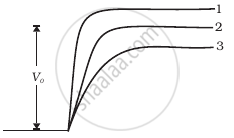
In Figure, Vo is the potential barrier across a p-n junction, when no battery is connected across the junction ______.
Consider an npn transistor with its base-emitter junction forward biased and collector base junction reverse biased. Which of the following statements are true?
- Electrons crossover from emitter to collector.
- Holes move from base to collector.
- Electrons move from emitter to base.
- Electrons from emitter move out of base without going to the collector.
Consider an npn transistor with its base-emitter junction forward biased and collector base junction reverse biased. Which of the following statements are true?
- Electrons crossover from emitter to collector.
- Holes move from base to collector.
- Electrons move from emitter to base.
- Electrons from emitter move out of base without going to the collector.
Draw the circuit arrangement for studying V-I characteristics of a p-n junction diode in (i) forward biasing and (ii) reverse biasing. Draw the typical V-I characteristics of a silicon diode.
