Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
(i) Explain with the help of a diagram the formation of depletion region and barrier potential in a pn junction.
उत्तर
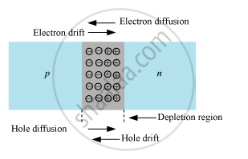
(i) In a p−n junction, a p-type and an n-type material are joined together. The concentration of holes is higher in p-type material as compared to that in n-type material. Therefore, there is a concentration gradient between the p-type and n-type materials. As a result of this concentration gradient, holes move from p-side to n-side (p → n) by the process of diffusion. Similarly, electrons move from n-side to p-side (n → p).
As the holes diffuse from p-side, they leave ionised spaces (negatively charged) on p-side near the junction. These ionised spaces are immobile. Hence, a negative space-charge region is formed on the p-side near the junction. Similarly, a positive space-charge region is formed on the n-side. These two space-charge regions on either sides of the junction constitute what is called a depletion layer.
Since the n-side loses electrons and p-side gains electrons, a potential difference is developed across the junction of the two regions. This potential difference tends to oppose further motion of electrons from the n-region into the p-region. The same happens for holes too. The reverse polarity of this potential opposes further flow of carriers and is thus called the barrier potential
संबंधित प्रश्न
What happens when a forward bias is applied to a p-n junction?
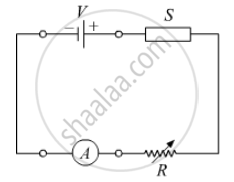
In the following diagram 'S' is a semiconductor. Would you increase or decrease the value of R to keep the reading of the ammeter A constant when S is heated? Give reason for your answer.
With reference to a semiconductor diode, what is meant by:
(i) Forward bias
(ii) Reverse bias
(iii) Depletion region
What are the applications of p - n Junction diode?
Depletion layer in p - n junction diode consists of
Figure shows the transfer characteristics of a base biased CE transistor. Which of the following statements are true?

At Vi = 0.4 V, transistor is in active state.
At Vi = 1 V, it can be used as an amplifier.
At Vi = 0.5 V, it can be used as a switch turned off.
At Vi = 2.5 V, it can be used as a switch turned on.
The breakdown in a reverse biased p–n junction diode is more likely to occur due to ______.
- large velocity of the minority charge carriers if the doping concentration is small.
- large velocity of the minority charge carriers if the doping concentration is large.
- strong electric field in a depletion region if the doping concentration is small.
- strong electric field in the depletion region if the doping concentration is large.
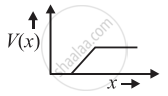
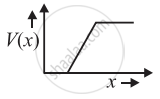
The graph of potential barrier versus width of depletion region for an unbiased diode is shown in graph A. In comparison to A, graphs B and C are obtained after biasing the diode in different ways. Identify the type of biasing in B and C and justify your answer
| ‘A’ | ‘B’ | ‘C’ |
 |
 |
 |
Draw V-I characteristics of a p-n Junction diode.
With reference to a semiconductor diode, define the potential barrier.
