Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
(i) Explain with the help of a diagram the formation of depletion region and barrier potential in a pn junction.
Solution
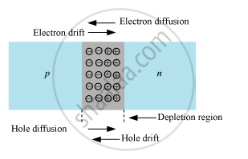
(i) In a p−n junction, a p-type and an n-type material are joined together. The concentration of holes is higher in p-type material as compared to that in n-type material. Therefore, there is a concentration gradient between the p-type and n-type materials. As a result of this concentration gradient, holes move from p-side to n-side (p → n) by the process of diffusion. Similarly, electrons move from n-side to p-side (n → p).
As the holes diffuse from p-side, they leave ionised spaces (negatively charged) on p-side near the junction. These ionised spaces are immobile. Hence, a negative space-charge region is formed on the p-side near the junction. Similarly, a positive space-charge region is formed on the n-side. These two space-charge regions on either sides of the junction constitute what is called a depletion layer.
Since the n-side loses electrons and p-side gains electrons, a potential difference is developed across the junction of the two regions. This potential difference tends to oppose further motion of electrons from the n-region into the p-region. The same happens for holes too. The reverse polarity of this potential opposes further flow of carriers and is thus called the barrier potential
RELATED QUESTIONS
What happens when a forward bias is applied to a p-n junction?
With reference to semiconductor devices, define a p-type semiconductor and a Zener diode.
What is the use of Zener diode?
Show on a graph, the variation of resistivity with temperature for a typical semiconductor.
In a photo diode, the conductive increases when the material is exposed to light. It is found that the conductivity changes only if the wavelength is less than 620 nm. What is the band gap?
(Use Planck constant h = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, Boltzmann constant k = 8·62 × 10-5 eV/K.)
The gain factor of an amplifier in increased from 10 to 12 as the load resistance is changed from 4 kΩ to 8 kΩ. Calculate (a) the amplification factor and (b) the plate resistance.
With reference to Semiconductor Physics,
Name the diode that emits spontaneous radiation when forward biased.
When we apply reverse biased to a junction diode, it
Use a transistor as an amplition
Avalanche breakdown is due to ______.
