Commerce (English Medium)
Science (English Medium)
Arts (English Medium)
Academic Year: 2015-2016
Date & Time: 5th March 2016, 10:30 am
Duration: 3h
Advertisements
In what way is the behaviour of a diamagnetic material different from that of a paramagnetic, when kept in an external magnetic field?
Chapter: [0.05] Magnetism and Matter
The plot of the variation of potential difference across a combination of three identical cells in series, versus current is shown below. What is the emf and internal resistance of each cell ?
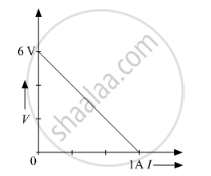
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
A charge 'q' is moved from a point A above a dipole of dipole moment 'p' to a point B below the dipole in equatorial plane without acceleration. Find the work done in the process.
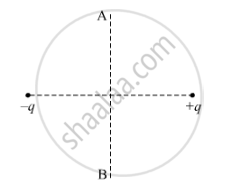
Chapter: [0.05] Magnetism and Matter
Name the essential components of a communication system.
Chapter: [0.15] Communication Systems
Calculate the de-Broglie wavelength of the electron orbitting in the n = 2 state of hydrogen atom.
Chapter: [0.12] Atoms
A battery of emf 12 V and internal resistance 2 Ω is connected to a 4 Ω resistor as shown in the figure.
(a) Show that a voltmeter when placed across the cell and across the resistor, in turn, gives the same reading.
(b) To record the voltage and the current in the circuit, why is voltmeter placed in parallel and ammeter in series in the circuit?
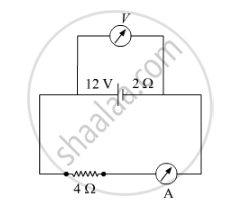
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
How would the ionization energy change when the electron in the hydrogen atom is replaced by a particle of mass 200 times that of the electron but having the same charge?
Chapter: [0.12] Atoms
Calculate the shortest wavelength of the spectral lines emitted in Balmer series.
[Given Rydberg constant, R = 107 m–1]
Chapter: [0.12] Atoms
Define modulation index.
Chapter: [0.15] Communication Systems
Why is Modulation index kept low?
Chapter: [0.15] Communication Systems
What is the role of a bandpass filter?
Chapter: [0.15] Communication Systems
A ray PQ incident normally on the refracting face BA is refracted in the prism BAC made of material of refractive index 1.5. Complete the path of ray through the prism. From which face will the ray emerge? Justify your answer.
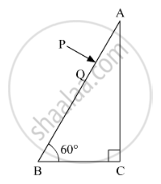
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Advertisements
Derive an expression for drift velocity of free electrons.
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
How does drift velocity of electrons in a metallic conductor vary with increase in temperature? Explain.
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
(a) Write the basic nuclear process involved in the emission of β+ in a symbolic form, by a radioactive nucleus.
(b) In the reactions given below:
(i)`""_16^11C->_y^zB+x+v`
(ii)`""_6^12C+_6^12C->_a^20 Ne + _b^c He`
Find the values of x, y, and z and a, b and c.
Chapter: [0.13] Nuclei
Sketch the graphs showing variation of stopping potential with frequency of incident radiations for two photosensitive materials A and B having threshold frequencies vA > vB.
(i) In which case is the stopping potential more and why?
(ii) Does the slope of the graph depend on the nature of the material used? Explain.
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Draw a graph showing the variation of intensity (I) of polarised light transmitted by an analyzer with the angle (θ) between polariser and analyzer.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
What is the value of refractive index of a medium of polarising angle 60°?
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
Define an equipotential surface.
Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
Draw equipotential surfaces:
(1) in the case of a single point charge and
(2) in a constant electric field in Z-direction. Why are the equipotential surfaces about a single charge not equidistant?
(3) Can electric field exist tangential to an equipotential surface? Give reason
Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
Use Biot-Savart law to derive the expression for the magnetic field on the axis of a current carrying circular loop of radius R.
Draw the magnetic field lines due to a circular wire carrying current I.
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
Consider a plane wave front incident on a thin convex lens. Draw a proper diagram to show how the incident wave front traverses through the lens and after refraction focusses on the focal point of the lens, giving the shape of the emergent wave front.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
When monochromatic light is incident on a surface separating two media, the reflected and refracted light both have the same frequency as the incident frequency.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
When light travels from a rarer to a denser medium, the speed decreases. Does this decrease in speed imply a reduction in the energy carried by the wave?
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
In the wave picture of light, the intensity of light is determined by the square of the amplitude of the wave. What determines the intensity in the photon picture of light?
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
For a CE-transistor amplifier, the audio signal voltage across the collector resistance of 2 kΩ is 2 V. Suppose the current amplification factor of the transistor is 100, find the input signal voltage and base current if the base resistance is 1 kΩ.
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Why does a galvanometer show a momentary deflection at the time of charging or discharging a capacitor? Write the necessary expression to explain this observation.
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
Identify the part of the electromagnetic spectrum which is suitable for radar system used in aircraft navigation.
Chapter: [0.08] Electromagnetic Waves
Identify the part of the electromagnetic spectrum which is:
produced by bombarding a metal target by high speed electrons.
Chapter: [0.08] Electromagnetic Waves
(i) Which mode of propagation is used by shortwave broadcast services having frequency range from a few MHz upto 30 MHz? Explain diagrammatically how long distance communication can be achieved by this mode.
(ii) Why is there an upper limit to frequency of waves used in this mode?
Chapter: [0.15] Communication Systems
Advertisements
(i) Explain with the help of a diagram the formation of depletion region and barrier potential in a pn junction.
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Draw the circuit diagram of a half wave rectifier and explain its working.
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
When an AC source is connected to an ideal inductor show that the average power supplied by the source over a complete cycle is zero.
Chapter: [0.07] Alternating Current
A lamp is connected in series with an inductor and an AC source. What happens to the brightness of the lamp when the key is plugged in and an iron rod is inserted inside the inductor? Explain.
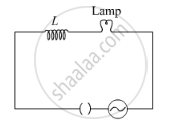
Chapter: [0.07] Alternating Current
Ram is a student of class X in a village school. His uncle gifted him a bicycle with a dynamo fitted in it. He was very excited to get it. While cycling during night, he could light the bulb and see the objects on the road. He, however, did not know how this device works. he asked this question to his teacher. The teacher considered it an opportunity to explain the working to the whole class.
Answer the following questions:
(a) State the principle and working of a dynamo.
(b) Write two values each displayed by Ram and his school teacher.
Chapter: [0.06] Electromagnetic Induction
(i) Derive the mathematical relation between refractive indices n1 and n2 of two radii and radius of curvature R for refraction at a convex spherical surface. Consider the object to be a point since lying on the principle axis in rarer medium of refractive index n1 and a real image formed in the denser medium of refractive index n2. Hence, derive lens maker's formula.
(ii) Light from a point source in air falls on a convex spherical glass surface of refractive index 1.5 and radius of curvature 20 cm. The distance of light source from the glass surface is 100 cm. At what position is the image formed?
Chapter:
Draw a labeled ray diagram to obtain the real image formed by an astronomical telescope in normal adjustment position. Define its magnifying power.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
You are given three lenses of power 0.5 D, 4 D, and 10 D to design a telescope.
1) Which lenses should be used as objective and eyepiece? Justify your answer.
2) Why is the aperture of the objective preferred to be large?
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Use Gauss's law to find the electric field due to a uniformly charged infinite plane sheet. What is the direction of field for positive and negative charge densities?
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
Find the ratio of the potential differences that must be applied across the parallel and series combination of two capacitors C1 and C2 with their capacitances in the ratio 1 : 2 so that the energy stored in the two cases becomes the same.
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
(i) If two similar large plates, each of area A having surface charge densities +σ and –σ are separated by a distance d in air, find the expressions for
(a) field at points between the two plates and on outer side of the plates. Specify the direction of the field in each case.
(b) the potential difference between the plates.
(c) the capacitance of the capacitor so formed.
(ii) Two metallic spheres of Radii R and 2R are charged so that both of these have same surface charge density σ. If they are connected to each other with a conducting wire, inn which direction will the charge flow and why?
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
Draw a labeled diagram of a step-down transformer.
Chapter: [0.07] Alternating Current
State the principle of the step-down transformer and its working.
Chapter: [0.07] Alternating Current
Express the turn ratio in terms of voltages.
Chapter: [0.07] Alternating Current
Find the ratio of primary and secondary currents in terms of turn ratio in an ideal transformer.
Chapter: [0.07] Alternating Current
How much current is drawn by the primary of a transformer connected to 220 V supply when it delivers power to a 110 V − 550 W refrigerator?
Chapter: [0.07] Alternating Current
Explain the meaning of the term mutual inductance.
Chapter: [0.06] Electromagnetic Induction
Consider two concentric circular coils, one of radius r1 and the other of radius r2 (r1 < r2) placed coaxially with centers coinciding with each other. Obtain the expression for the mutual inductance of the arrangement.
Chapter: [0.06] Electromagnetic Induction
A rectangular coil of area A, having the number of turns N is rotated at 'f' revolutions per second in a uniform magnetic field B, the field being perpendicular to the coil. Prove that the maximum emf induced in the coil is 2 πf NBA.
Chapter: [0.06] Electromagnetic Induction
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CBSE previous year question papers Class 12 Physics with solutions 2015 - 2016
Previous year Question paper for CBSE Class 12 Physics-2016 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Physics, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CBSE Class 12.
How CBSE Class 12 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Physics will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
