Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
When an electric field is applied across a semiconductor ______.
- electrons move from lower energy level to higher energy level in the conduction band.
- electrons move from higher energy level to lower energy level in the conduction band.
- holes in the valence band move from higher energy level to lower energy level.
- holes in the valence band move from lower energy level to higher energy level.
पर्याय
a and b
b and c
d and a
a and c
उत्तर
a and c
Explanation:
In the valence band electrons are not capable of gaining energy from the external electric fields. While in the conduction band the electrons can gain energy from the external electric field.
When an electric field is applied across a semiconductor, the electrons in the conduction band (which is partially filled with electrons) get accelerated and acquire energy. They move from lower energy levels to higher energy levels. While the holes in the valence band move from higher energy level to lower energy level, where they will be having more energy.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain the working of P-N junction diode in forward and reverse biased mode.
What causes the setting up of high electric field even for small reverse bias voltage across the diode?
With reference to semi-conductors answer the following :
(i) What is the change in the resistance of the semi-conductor with increase in temperature ?
(ii) Name the majority charge carriers in n-type semi-conductor.
(iii) What is meant by doping ?
A plate current of 10 mA is obtained when 60 volts are applied across a diode tube. Assuming the Langmuir-Child relation \[i_p \infty V_p^{3/2}\] to hold, find the dynamic resistance rp in this operating condition.
A triode value operates at Vp = 225 V and Vg = −0.5 V.
The plate current remains unchanged if the plate voltage is increased to 250 V and the grid voltage is decreased to −2.5 V. Calculate the amplification factor.
What are the applications of p - n Junction diode?
The current through an ideal PN-junction shown in the following circuit diagram will be:
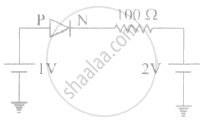
Differentiate between the threshold voltage and the breakdown voltage for a diode.
Draw the circuit arrangement for studying V-I characteristics of a p-n junction diode in (i) forward biasing and (ii) reverse biasing. Draw the typical V-I characteristics of a silicon diode.
An ideal PN junction diode offers ______.
