Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Figure shows the transfer characteristics of a base biased CE transistor. Which of the following statements are true?

At Vi = 0.4 V, transistor is in active state.
At Vi = 1 V, it can be used as an amplifier.
At Vi = 0.5 V, it can be used as a switch turned off.
At Vi = 2.5 V, it can be used as a switch turned on.
Options
a and c
a, c and d
b and c
b, c and d
Solution
b, c and d
Explanation:
According to the above graph transfer characteristics of a base biased common emitter transistor, we note that.
- When Vi= 0.4 V, the output voltage remain same and there is no collection current. So, the transistor circuit is not in an active state.
- When Vi = 1 V (This is in between 0.6 V to 2 V), the transistor circuit is in an active state and when input is increasing output is decreasing because when CE is used as an amplifier input and output voltages are 180° out of phase. Then it is used as an amplifier.
- When Vi = 0.5 V, there is no collector current. The transistor is in a cut-off state. The transistor circuit can be used as a switch to be turned off.
- When Vi = 2.5 V, the collector current becomes maximum and the transistor is in a saturation state and can be used as a switch turned on state.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Draw a labelled diagram of a full wave rectifier. Show how output voltage varies with time if the input voltage is a sinusoidal voltage.
When we apply reverse biased to a junction diode, it
Use a transistor as an amplition
On increasing the reverse biases voltage to a large value in a P – N junction diode-current
A Zener of power rating 1 W is to be used as a voltage regulator. If zener has a breakdown of 5 V and it has to regulate voltage which fluctuated between 3 V and 7 V, what should be the value of Rs for safe operation (Figure)?

The graph of potential barrier versus width of depletion region for an unbiased diode is shown in graph A. In comparison to A, graphs B and C are obtained after biasing the diode in different ways. Identify the type of biasing in B and C and justify your answer
| ‘A’ | ‘B’ | ‘C’ |
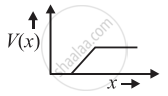 |
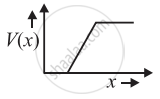 |
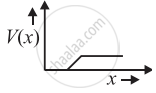 |
Answer the following giving reasons:
A p-n junction diode is damaged by a strong current.
Draw the circuit arrangement for studying V-I characteristics of a p-n junction diode in (i) forward biasing and (ii) reverse biasing. Draw the typical V-I characteristics of a silicon diode.
What is meant by forward biasing of a semiconductor diode?
An ideal PN junction diode offers ______.
