Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Consider an npn transistor with its base-emitter junction forward biased and collector base junction reverse biased. Which of the following statements are true?
- Electrons crossover from emitter to collector.
- Holes move from base to collector.
- Electrons move from emitter to base.
- Electrons from emitter move out of base without going to the collector.
Options
d and a
a and b
b and c
a and c
Solution
a and c
Explanation:
Transistor: A junction transistor is formed by sandwiching 2 thin layer of P-type semiconductors between two N-type semiconductors. or by sandwiching a thin taver of V-type semiconductors between two P-type semiconductors.
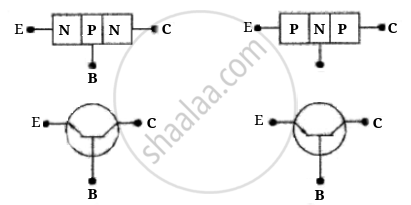
E — Emitter (emits majority charge carriers)
C — Collects majority charge carriers
B — Base (provide proper interaction between E and C)

In normal operation base-emitter is forward biased, i.e., the positive pole of the emitter-base battery is connected to the base and its negative pole is connected to the emitter. And collector-base junction is reverse biased, i.e., the positive pole of the collector base battery is connected to the collector and the negative pole to base. Thus, electron moves from emitter to base and crossovers from emitter to collector.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Show on a graph, the variation of resistivity with temperature for a typical semiconductor.
The dynamic plate resistance of a triode value is 10 kΩ. Find the change in the plate current if the plate voltage is changed from 200 V to 220 V.
The gain factor of an amplifier in increased from 10 to 12 as the load resistance is changed from 4 kΩ to 8 kΩ. Calculate (a) the amplification factor and (b) the plate resistance.
Answer the following question.
Why photodiodes are required to operate in reverse bias? Explain.
When we apply reverse biased to a junction diode, it
The expected energy of the electron at absolute zero is called:-
On increasing the reverse biases voltage to a large value in a P – N junction diode-current
In the circuit shown in figure, if the diode forward voltage drop is 0.3 V, the voltage difference between A and B is ______.

Explain the formation of the barrier potential in a p-n junction.
Draw the circuit arrangement for studying V-I characteristics of a p-n junction diode in (i) forward biasing and (ii) reverse biasing. Draw the typical V-I characteristics of a silicon diode.
