Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
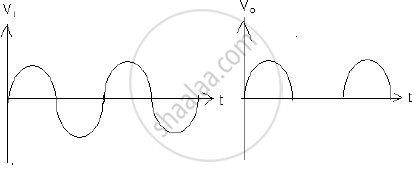
With the help of neat labelled circuit diagram explain the working of half wave rectifier using semiconductor diode. Draw the input and output waveforms.
उत्तर
A device which converts A.C. to D.C. is called rectifier. In this case output exists only for half cycle hence it is called half wave rectifier. Construction: The circuit diagram of a half wave rectifier using a junctiondiode is as shown in fig. The alternating voltage source is connected to the primary coil of a transformer. The secondary coil is connected to the diode in series with a resistance RL called the load resistance

T=Transformer
D=Diode
V0=output voltage
v1=input votage
RL=load resistance
Working: In first cycle of input voltage, the anode of the diode is positive potential w.r.t. cathode. Hence the diode is in forward-biased. Hence it conduct current. The current flows through load resistance giving voltage drop iRL. This voltage drop is called output voltage. During next half cycle the anode of diode is in negative potential w.r.t. Hence it is in reversed-biased. Hence it does not conduct the current. Hence current does not flow through load resistance giving no P.D. across it. Hence output voltage is unidirectional. It is called as D.C.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain the working of P-N junction diode in forward and reverse biased mode.
What happens when a forward bias is applied to a p-n junction?
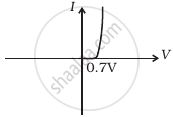
In the following diagram 'S' is a semiconductor. Would you increase or decrease the value of R to keep the reading of the ammeter A constant when S is heated? Give reason for your answer.
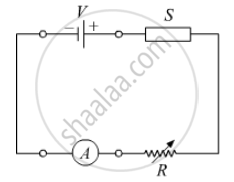
In the following diagram, is the junction diode forward biased or reverse biased ?
With reference to semiconductor devices, define a p-type semiconductor and a Zener diode.
In a photo diode, the conductive increases when the material is exposed to light. It is found that the conductivity changes only if the wavelength is less than 620 nm. What is the band gap?
(Use Planck constant h = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, Boltzmann constant k = 8·62 × 10-5 eV/K.)
A plate current of 10 mA is obtained when 60 volts are applied across a diode tube. Assuming the Langmuir-Child relation \[i_p \infty V_p^{3/2}\] to hold, find the dynamic resistance rp in this operating condition.
The plate current in a diode is 20 mA when the plate voltage is 50 V or 60 V. What will be the current if the plate voltage is 70 V?
A triode value operates at Vp = 225 V and Vg = −0.5 V.
The plate current remains unchanged if the plate voltage is increased to 250 V and the grid voltage is decreased to −2.5 V. Calculate the amplification factor.
The dynamic plate resistance of a triode value is 10 kΩ. Find the change in the plate current if the plate voltage is changed from 200 V to 220 V.
The gain factor of an amplifier in increased from 10 to 12 as the load resistance is changed from 4 kΩ to 8 kΩ. Calculate (a) the amplification factor and (b) the plate resistance.
With reference to a semiconductor diode, what is meant by:
(i) Forward bias
(ii) Reverse bias
(iii) Depletion region
Answer the following question.
Why photodiodes are required to operate in reverse bias? Explain.
What are the applications of p - n Junction diode?
Of the diodes shown in the following diagrams, which one is reverse biased?
Depletion layer in p - n junction diode consists of
The nature of binding for a crystal with alternate and evenly spaced positive and negatively ions is
In forward bias width of potential barrier in a p + n junction diode
In a semiconductor diode, the barrier potential offers opposition to only
Avalanche breakdown is due to ______.
In the circuit shown in figure, if the diode forward voltage drop is 0.3 V, the voltage difference between A and B is ______.

In the depletion region of a diode ______.
- there are no mobile charges.
- equal number of holes and electrons exist, making the region neutral.
- recombination of holes and electrons has taken place.
- immobile charged ions exist.
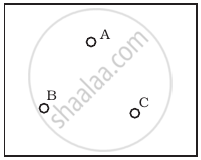
Consider a box with three terminals on top of it as shown in figure (a):
 (a) |
Three components namely, two germanium diodes and one resistor are connected across these three terminals in some arrangement. A student performs an experiment in which any two of these three terminals are connected in the circuit shown in figure (b).
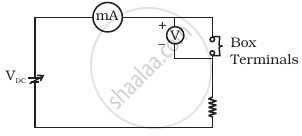 (b) |
The student obtains graphs of current-voltage characteristics for unknown combination of components between the two terminals connected in the circuit. The graphs are
(i) when A is positive and B is negative
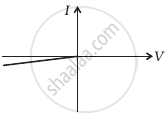 (c) |
(ii) when A is negative and B is positive
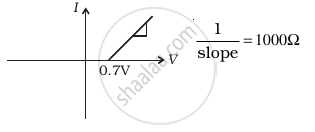 (d) |
(iii) When B is negative and C is positive
|
(e) |
(iv) When B is positive and C is negative
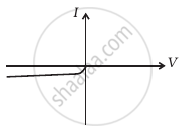 (f) |
(v) When A is positive and C is negative
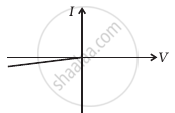 (g) |
(vi) When A is negative and C is positive
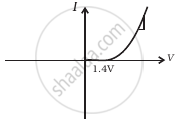 (h) |
From these graphs of current-voltage characteristics shown in figure (c) to (h), determine the arrangement of components between A, B and C.
Differentiate between the threshold voltage and the breakdown voltage for a diode.
Write the property of a junction diode which makes it suitable for rectification of ac voltages.
Answer the following giving reasons:
A p-n junction diode is damaged by a strong current.
Draw the circuit arrangement for studying V-I characteristics of a p-n junction diode in (i) forward biasing and (ii) reverse biasing. Draw the typical V-I characteristics of a silicon diode.
Describe briefly the following term:
breakdown voltage in reverse biasing
Read the following paragraph and answer the questions that follow.
| A semiconductor diode is basically a pn junction with metallic contacts provided at the ends for the application of an external voltage. It is a two-terminal device. When an external voltage is applied across a semiconductor diode such that the p-side is connected to the positive terminal of the battery and the n-side to the negative terminal, it is said to be forward-biased. When an external voltage is applied across the diode such that the n-side is positive and the p-side is negative, it is said to be reverse-biased. An ideal diode is one whose resistance in forward biasing is zero and the resistance is infinite in reverse biasing. When the diode is forward biased, it is found that beyond forward voltage called knee voltage, the conductivity is very high. When the biasing voltage is more than the knee voltage the potential barrier is overcome and the current increases rapidly with an increase in forward voltage. When the diode is reverse biased, the reverse bias voltage produces a very small current of about a few microamperes which almost remains constant with bias. This small current is a reverse saturation current. |
- In the given figure, a diode D is connected to an external resistance R = 100 Ω and an emf of 3.5 V. If the barrier potential developed across the diode is 0.5 V, the current in the circuit will be:

(a) 40 mA
(b) 20 mA
(c) 35 mA
(d) 30 mA - In which of the following figures, the pn diode is reverse biased?
(a)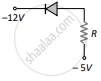
(b)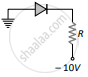
(c)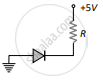
(d)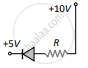
- Based on the V-I characteristics of the diode, we can classify the diode as:
(a) bilateral device
(b) ohmic device
(c) non-ohmic device
(d) passive element
OR
Two identical PN junctions can be connected in series by three different methods as shown in the figure. If the potential difference in the junctions is the same, then the correct connections will be:
(a) in the circuits (1) and (2)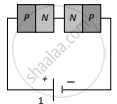
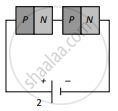
(b) in the circuits (2) and (3)
(c) in the circuits (1) and (3)
(d) only in the circuit (1) 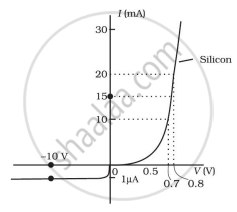
The V-I characteristic of a diode is shown in the figure. The ratio of the resistance of the diode at I = 15 mA to the resistance at V = -10 V is
(a) 100
(b) 106
(c) 10
(d) 10-6
What is meant by forward biasing of a semiconductor diode?