Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
With the help of neat labelled circuit diagram explain the working of half wave rectifier using semiconductor diode. Draw the input and output waveforms.
Solution
A device which converts A.C. to D.C. is called rectifier. In this case output exists only for half cycle hence it is called half wave rectifier. Construction: The circuit diagram of a half wave rectifier using a junctiondiode is as shown in fig. The alternating voltage source is connected to the primary coil of a transformer. The secondary coil is connected to the diode in series with a resistance RL called the load resistance

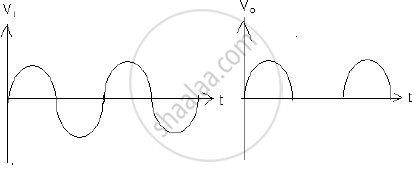
T=Transformer
D=Diode
V0=output voltage
v1=input votage
RL=load resistance
Working: In first cycle of input voltage, the anode of the diode is positive potential w.r.t. cathode. Hence the diode is in forward-biased. Hence it conduct current. The current flows through load resistance giving voltage drop iRL. This voltage drop is called output voltage. During next half cycle the anode of diode is in negative potential w.r.t. Hence it is in reversed-biased. Hence it does not conduct the current. Hence current does not flow through load resistance giving no P.D. across it. Hence output voltage is unidirectional. It is called as D.C.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What is the use of Zener diode?
Why is a zener diode considered as a special purpose semiconductor diode?
In a photo diode, the conductive increases when the material is exposed to light. It is found that the conductivity changes only if the wavelength is less than 620 nm. What is the band gap?
(Use Planck constant h = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, Boltzmann constant k = 8·62 × 10-5 eV/K.)
A plate current of 10 mA is obtained when 60 volts are applied across a diode tube. Assuming the Langmuir-Child relation \[i_p \infty V_p^{3/2}\] to hold, find the dynamic resistance rp in this operating condition.
A triode value operates at Vp = 225 V and Vg = −0.5 V.
The plate current remains unchanged if the plate voltage is increased to 250 V and the grid voltage is decreased to −2.5 V. Calculate the amplification factor.
The dynamic plate resistance of a triode value is 10 kΩ. Find the change in the plate current if the plate voltage is changed from 200 V to 220 V.
In semiconductor physics, what is meant by:
(i) rectifier
(ii) an amplifier
(iii) an oscillator
What are the applications of p - n Junction diode?
The current through an ideal PN-junction shown in the following circuit diagram will be:
The drift current in a p-n junction is from the ______.
A – pn junction has a depletion layer of thickness .of the order of
When we apply reverse biased to a junction diode, it
The nature of binding for a crystal with alternate and evenly spaced positive and negatively ions is
In a semiconductor diode, the barrier potential offers opposition to only
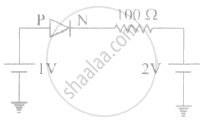
In the circuit shown in figure, if the diode forward voltage drop is 0.3 V, the voltage difference between A and B is ______.

When an electric field is applied across a semiconductor ______.
- electrons move from lower energy level to higher energy level in the conduction band.
- electrons move from higher energy level to lower energy level in the conduction band.
- holes in the valence band move from higher energy level to lower energy level.
- holes in the valence band move from lower energy level to higher energy level.
Consider an npn transistor with its base-emitter junction forward biased and collector base junction reverse biased. Which of the following statements are true?
- Electrons crossover from emitter to collector.
- Holes move from base to collector.
- Electrons move from emitter to base.
- Electrons from emitter move out of base without going to the collector.
Figure shows the transfer characteristics of a base biased CE transistor. Which of the following statements are true?

At Vi = 0.4 V, transistor is in active state.
At Vi = 1 V, it can be used as an amplifier.
At Vi = 0.5 V, it can be used as a switch turned off.
At Vi = 2.5 V, it can be used as a switch turned on.
The breakdown in a reverse biased p–n junction diode is more likely to occur due to ______.
- large velocity of the minority charge carriers if the doping concentration is small.
- large velocity of the minority charge carriers if the doping concentration is large.
- strong electric field in a depletion region if the doping concentration is small.
- strong electric field in the depletion region if the doping concentration is large.
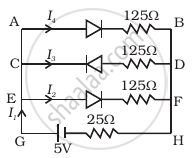
If each diode in figure has a forward bias resistance of 25 Ω and infinite resistance in reverse bias, what will be the values of the current I1, I2, I3 and I4?
In the circuit shown in figure, when the input voltage of the base resistance is 10 V, Vbe is zero and Vce is also zero. Find the values of Ib, Ic and β.
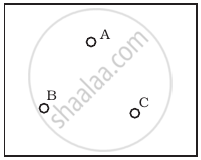
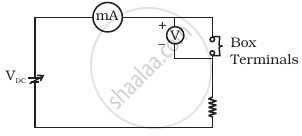
Consider a box with three terminals on top of it as shown in figure (a):
 (a) |
Three components namely, two germanium diodes and one resistor are connected across these three terminals in some arrangement. A student performs an experiment in which any two of these three terminals are connected in the circuit shown in figure (b).
 (b) |
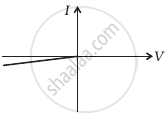
The student obtains graphs of current-voltage characteristics for unknown combination of components between the two terminals connected in the circuit. The graphs are
(i) when A is positive and B is negative
 (c) |
(ii) when A is negative and B is positive
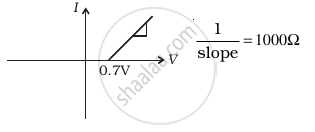 (d) |
(iii) When B is negative and C is positive
|
(e) |
(iv) When B is positive and C is negative
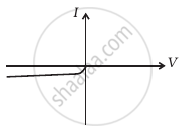 (f) |
(v) When A is positive and C is negative
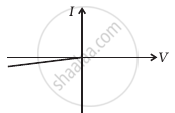 (g) |
(vi) When A is negative and C is positive
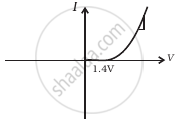 (h) |
From these graphs of current-voltage characteristics shown in figure (c) to (h), determine the arrangement of components between A, B and C.
Explain the formation of the barrier potential in a p-n junction.
A semiconductor device is connected in series with a battery, an ammeter and a resistor. A current flows in the circuit. If. the polarity of the battery is reversed, the current in the circuit almost becomes zero. The device is a/an ______.
With reference to a semiconductor diode, define the potential barrier.
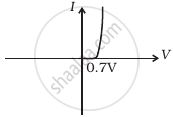
Draw a labelled characteristic curve (l-V graph) for a semiconductor diode during forward bias.