Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In semiconductor physics, what is meant by:
(i) rectifier
(ii) an amplifier
(iii) an oscillator
Solution
(i) Rectifier: It is a device which converts alternating current into direct current.
(ii) Amplifier: An amplifier is a device which increases the energy of a weak signal by supplying energy from an external source. An amplifier increases the amplitude of a input signal.
(iii) Oscillator: An oscillator is a device which produces electrical oscillations of adjustable frequency and constant amplitude. An oscillator is basically an amplifier. A part of the output energy is fed back into the L-C circuit to produce sustained oscillations.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Plot a graph showing variation of current versus voltage for the material GaAs ?
Why is a zener diode considered as a special purpose semiconductor diode?
In a photo diode, the conductive increases when the material is exposed to light. It is found that the conductivity changes only if the wavelength is less than 620 nm. What is the band gap?
(Use Planck constant h = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, Boltzmann constant k = 8·62 × 10-5 eV/K.)
A triode value operates at Vp = 225 V and Vg = −0.5 V.
The plate current remains unchanged if the plate voltage is increased to 250 V and the grid voltage is decreased to −2.5 V. Calculate the amplification factor.
Answer the following question.
Why photodiodes are required to operate in reverse bias? Explain.
When we apply reverse biased to a junction diode, it
Figure shows the transfer characteristics of a base biased CE transistor. Which of the following statements are true?

At Vi = 0.4 V, transistor is in active state.
At Vi = 1 V, it can be used as an amplifier.
At Vi = 0.5 V, it can be used as a switch turned off.
At Vi = 2.5 V, it can be used as a switch turned on.
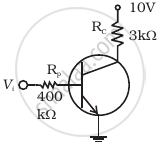
In the circuit shown in figure, when the input voltage of the base resistance is 10 V, Vbe is zero and Vce is also zero. Find the values of Ib, Ic and β.
Draw V-I characteristics of a p-n Junction diode.
Describe briefly the following term:
breakdown voltage in reverse biasing
