ISC (Commerce)
ISC (Arts)
ISC (Science)
Academic Year: 2013-2014
Date: March 2014
Advertisements
The intensity of the electric field at a point at a perpendicular distance ‘r’ from an infinite line charge, having linear charge density ‘λ’ is given by:
E = `(1/(4π∈_0))λ/r`
E = `(1/(4π∈_0)) (2λ)/r`
E = `(1/(4π∈_0)) λ/r^2`
E = `(1/(4π∈_0)) (2λ)/r^2`
Chapter: [0.011000000000000001] Electric Charges and Fields
If R1 and R2 are filament resistances of a 200 W and a 100 W bulb respectively, designed to operate on the same voltage, then:
R1 = R2
R2 = 2R1
R2 = 4R1
R1 = 4R2
Chapter: [0.02] Current Electricity
A metallic wire having a length of 2 m and weight of 4 x 10-3 N is found to remain at rest in a uniform and transverse magnetic field of 2 x 10-4 T. Current flowing through the wire is:
10 A
5 A
2 A
1 A
Chapter:
When a beam of white light is passed through sodium vapors and then through a spectrometer, spectrum so obtained has two dark lines present in the yellow region. This spectrum is called:
band spectrum
continuous spectrum
absorption spectrum of sodium
emission spectrum of sodium
Chapter: [0.081] Atoms
If l3 and l2 represent angular momenta of an orbiting electron in III and II Bohr orbits respectively, then l3: l2 is :
3: 2
9: 4
2: 3
4: 9
Chapter: [0.081] Atoms
A parallel plate air capacitor has a capacitance of 5 μF. It becomes 50 μF when a dielectric medium occupies the entire space between its two plates. What is the dielectric constant of the medium?
Chapter: [0.012] Electrostatic Potential, Potential Energy and Capacitance
Find the emf of the battery shown in the figure:
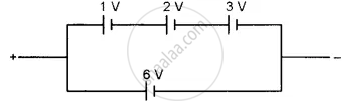
Chapter: [0.02] Current Electricity
Two substances A and B have their relative permeability slightly greater and slightly less than 1 respectively. What do you conclude about A and B as far as their magnetic materials are concerned?
Chapter: [0.032] Magnetism and Matter
When does a moving charged particle nor experience any force while moving through a uniform magnetic field?
Chapter: [0.031] Moving Charges and Magnetism
What is the turns ratio i.e., transformer ratio, ns: np, in an ideal transformer which in-creases ac voltage from 220 V to 33000 V?
Chapter: [0.042] Alternating Current
What is meant by coherent sources of light?
Chapter: [0.062] Wave Optics
A ray of light is incident on a transparent medium at a polarizing angle. What is the angle between the reflected ray and the refracted ray?
Chapter: [0.062] Wave Optics
Name the physical principle on which the working of optical fibers is based.
Chapter: [0.061] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
How does focal length of a convex lens change with increase in wavelength of incident light?
Chapter: [0.061] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
With reference to the photoelectric effect, what is meant by threshold wavelength?
Chapter: [0.07] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Advertisements
The half-life of a certain radioactive element is 3.465 days. Find its disintegration constant.
Chapter: [0.08199999999999999] Nuclei
Binding energy per nucleon for helium nucleus (2 He) is 7.0 MeV Find value of mass defect for helium nucleus
Chapter: [0.08199999999999999] Nuclei
Write one balanced reaction representing nuclear fusion.
Chapter: [0.08199999999999999] Nuclei
Draw the truth table of a NOR gate.
Chapter: [0.09] Electronic Devices
An electric dipole of dipole moment `vecP` is placed in a uniform electric field `vecE` with its axis inclined to the field. Write an expression for the torque `vecT` experienced by the dipole in vector form. Show diagrammatically how the dipole should be kept in the electric field so that the torque acting on it is:
- maximum
- Zero
Chapter: [0.011000000000000001] Electric Charges and Fields
You are provided with 8 μF capacitors. Show with the help of a diagram how you will arrange minimum number of them to get a resultant capacitance of 20 μF.
Chapter: [0.012] Electrostatic Potential, Potential Energy and Capacitance
Define temperature coefficient of resistance of the material of a conductor.
Chapter: [0.02] Current Electricity
Draw a labelled circuit diagram of a potentiometer to compare emfs of two cells. Write the working formula (Derivation not required).
Chapter: [0.02] Current Electricity
How much resistance should be connected to 15 Ω resistor shown in the circuit in figure below so that the points M and N are at the same potential:
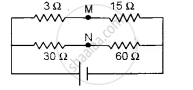
Chapter: [0.02] Current Electricity
With reference to free-electron theory of conductivity, explain the terms:
(a) Drift speed
(b) Relaxation time
Chapter: [0.02] Current Electricity
What is the colour code of a carbon resistor having a resistance of 470 Ω and a tolerance of 5%?
Chapter: [0.02] Current Electricity
State Tangent Law in magnetism.
Chapter: [0.032] Magnetism and Matter
At a certain temperature, a ferromagnetic material becomes paramagnetic. What is this temperature called?
Chapter: [0.032] Magnetism and Matter
State Biot Savart law.
Chapter: [0.031] Moving Charges and Magnetism
Find magnetic flux density at a point on the axis of a long solenoid having 5000 tums/m when it carrying a current of 2 A.
Chapter: [0.040999999999999995] Electromagnetic Induction
An alternating emf of 110 V is applied to a circuit containing a resistance R of 80 Ω and an inductor L in series. The current is found to lag behind the supply voltage by an angle 8 = tan-1 (3/4). Find the :
(i) Inductive reactance
(ii) Impedance of the circuit
(iii) Current flowing in the circuit
(iv) If the inductor has a coefficient of self-inductance of 0.1 H, what is the frequency of the applied emf?
Chapter: [0.040999999999999995] Electromagnetic Induction
Name the part of the electromagnetic spectrum which is:
Suitable for radar systems used in aircraft navigation.
Chapter: [0.05] Electromagnetic Waves
Name the part of the electromagnetic spectrum which is:
Produced by bombarding a metal target with high electrons.
Chapter: [0.05] Electromagnetic Waves
In Young’s double-slit experiment, using monochromatic light, fringes are obtained on a screen placed at some distance from the slits. If the screen is moved by 5 x 10-2 m towards the slits, the change in the fringe width is 3 x 10-5 m. If the distance between the two slits is 10-3 m, calculate the wavelength of the light used.
Chapter: [0.062] Wave Optics
Advertisements
State Brewster’s law of polarization of light.
Chapter: [0.062] Wave Optics
How will you identify with the help of an experiment whether a given beam of light is of polarized light or of unpolarized light?
Chapter: [0.062] Wave Optics
A narrow beam of monochromatic light, PQ, is incident normally on one face of an equiangular glass prism of refractive index 1.45. When the prism is immersed in a certain liquid, the ray makes a grazing emergence along the other face (See figure). Find the refractive index of this liquid. 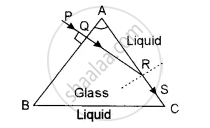
Chapter: [0.061] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
When two thin lenses of focal lengths f1 and f2 are kept coaxially and in contact, prove that their combined focal length ‘f’ is given by: `1/f = 1/f_1 + 1/f_2`
Chapter:
The figure below shows the positions of a point object O, two lenses, a plane mirror and the final image I which coincides with the object. The focal length of the convex lens is 20 cm. Calculate the focal length of the concave lens.
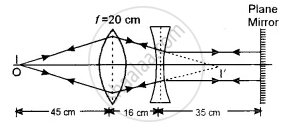
Chapter: [0.061] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
What is meant by the dispersive power of transparent material?
Chapter: [0.061] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Show that, two thin lenses kept in contact, form an achromatic doublet if they satisfy the condition: `ω/f + (w')/(f') = 0`
where the terms have their usual meaning.
Chapter:
Define the magnifying power of a microscope in terms of visual angle.
Chapter: [0.061] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
What is the advantage of a compound microscope over a simple microscope?
Chapter: [0.061] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
An astronomical telescope uses two lenses of powers 10 dioptres and 1 dioptre. If the final image of a distant object is formed at infinity, calculate the length of the telescope
Chapter: [0.061] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Answer the following questions with reference to Millikan’s oil drop experiment:
(i) What is an atomiser?
(ii)What is the use of an X-ray tube?
(iii) What is the unique property shown by the charge of an oil drop?
Chapter: [0.09] Electronic Devices
Write Einstein’s photoelectric equation.
Chapter: [0.07] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
If the frequency of the incident radiation is increased from 4 × 1015 Hz to 8 × 1015 Hz, by how much will the stopping potential for a given photosensitive surface go up?
Chapter: [0.07] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
What are matter waves?
Chapter: [0.07] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Show with the help of a labelled graph how their wavelength (λ) varies with their linear momentum (p).
Chapter: [0.07] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
The energy levels of an atom of a certain element are shown in the given figure. Which one of the transitions A, B, C, D or E will result in the emission of photons of electromagnetic radiation of wavelength 618.75 nm? Support your answer with mathematical calculations.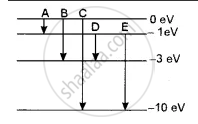
Chapter: [0.05] Electromagnetic Waves
Voltage applied between cathode and anode of an X-ray tube is 18 kV. Calculate the minimum wavelength of the X-rays produced.
Chapter: [0.09] Electronic Devices
In a nuclear reactor, what is the function of:
(i) The moderator
(ii) The control rods
(iii) The coolant
Chapter: [0.08199999999999999] Nuclei
The atomic mass of Uranium `""_92^238"U"` is 238.0508 u, while that of Thorium `""_90^234"Th"` is 234.0436u, and that of Helium `""_2^4"He"` "is 4.0026u. Alpha decay converts `""_92^238"U"` into `""_92^234"Th"` as, shown below:
`""_92^238"U" -> ( ""_90^234"Th" + ""_2^4"He" + "Energy" )`
Chapter: [0.08199999999999999] Nuclei
What is a neutrino?
Chapter: [0.08199999999999999] Nuclei
In semiconductor physics, what is meant by:
(i) rectifier
(ii) an amplifier
(iii) an oscillator
Chapter: [0.09] Electronic Devices
With the help of a diagram, show how you can use several NAND gates to obtain an OR gate.
Useful Constants and Relations :
| 1. Speed of Light in Vacuum | (c) = 3.00 x 108 m/s |
| 2. Charge of a proton | (e) = 1.60 x 10-19C |
| 3. Planck's Constant | (h) = 6.6 x 10-34 Js |
| 4. Permeability of vacuum | (μ0) = 4π x 10-7 Hm-1 |
| 5. Electron Volt | (1eV ) = 1.6 x 10 |
| 6. Unified Atomic Mass Unit | (1u) = 931 MeV |
| (π) = 3.14 | |
| ( ln 2 ) = 0.693 |
Chapter: [0.09] Electronic Devices
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CISCE previous year question papers Class 12 Physics (Theory) with solutions 2013 - 2014
Previous year Question paper for CISCE Class 12 -2014 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Physics (Theory), you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CISCE Class 12.
How CISCE Class 12 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Physics (Theory) will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
