Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
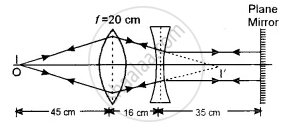
The figure below shows the positions of a point object O, two lenses, a plane mirror and the final image I which coincides with the object. The focal length of the convex lens is 20 cm. Calculate the focal length of the concave lens.
Solution
Since the image of the object coincides with the object itself, the rays of light passing through the lens combination strike the mirror normally. The point I’ where the rays of light are converged by the convex lens must be the focus of the concave lens because the emergent rays are parallel to the principal axis. For the convex lens.
u = - 45 cm, f = 20 cm, v = ?
Now, `1/v - 1/u = 1/f`
`1/v + 1/45 = 1/20`
`1/v = 1/20 - 1/45 = ( 9 - 4 )/180 = 5/180`
∴ v = `180/5` = 36 cm
Now, distance between the two lenses is 16 cm.
∴ Focal length of the concave lens = 36 – 16 = 20 cm
Since the lens is concave, f = – 20 cm
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Use the mirror equation to deduce that the virtual image produced by a convex mirror is always diminished in size and is located between the focus and the pole.
Use the mirror equation to deduce that an object placed between the pole and focus of a concave mirror produces a virtual and enlarged image.
Use the mirror equation to show a convex mirror always produces a virtual image independent of the location of the object ?
following Figure shows two rays A and B being reflected by a mirror and going as A' and B'. The mirror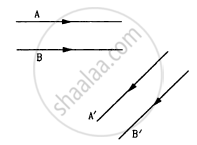
The rays of different colours fail to converge at a point after going through a converging lens. This defect is called
A cylindrical vessel of diameter 12 cm contains 800π cm3 of water. A cylindrical glass piece of diameter 8.0 cm and height 8.0 cm is placed in the vessel. If the bottom of the vessel under the glass piece is seen by the paraxial rays (see figure), locate its image. The index of refraction of glass is 1.50 and that of water is 1.33.

A light ray is incident at an angle of 45° with the normal to a √2 cm thick plate (μ = 2.0). Find the shift in the path of the light as it emerges out from the plate.
A light ray, going through a prism with the angle of prism 60°, is found to deviate by 30°. What limit on the refractive index can be put from these data?
Name the physical principle on which the working of optical fibers is based.
A convex lens of focal length 15 cm is placed coaxially in front of a convex mirror. The lens is 5 cm from the pole of the mirror. When an object is placed on the axis at a distance of 20 cm from the lens, it is found that the image coincides with the object. Calculate the radius of curvature of the mirror - (consider all-optical event):
