Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
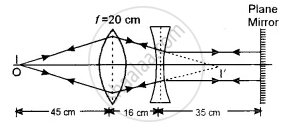
The figure below shows the positions of a point object O, two lenses, a plane mirror and the final image I which coincides with the object. The focal length of the convex lens is 20 cm. Calculate the focal length of the concave lens.
उत्तर
Since the image of the object coincides with the object itself, the rays of light passing through the lens combination strike the mirror normally. The point I’ where the rays of light are converged by the convex lens must be the focus of the concave lens because the emergent rays are parallel to the principal axis. For the convex lens.
u = - 45 cm, f = 20 cm, v = ?
Now, `1/v - 1/u = 1/f`
`1/v + 1/45 = 1/20`
`1/v = 1/20 - 1/45 = ( 9 - 4 )/180 = 5/180`
∴ v = `180/5` = 36 cm
Now, distance between the two lenses is 16 cm.
∴ Focal length of the concave lens = 36 – 16 = 20 cm
Since the lens is concave, f = – 20 cm
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Using mirror formula, explain why does a convex mirror always produce a virtual image.
Use the mirror equation to show that an object placed between f and 2f of a concave mirror forms an image beyond 2f.
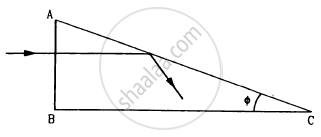
A light ray is incident normally on the face AB of a right-angled prism ABC (μ = 1.50) as shown in figure. What is the largest angle ϕ for which the light ray is totally reflected at the surface AC?
A light ray, going through a prism with the angle of prism 60°, is found to deviate by 30°. What limit on the refractive index can be put from these data?
Write any one use for each of the following mirrors :
(a) Convex
(b) Concave
Name the physical principle on which the working of optical fibers is based.
For paraxial rays, show that the focal length of a spherical mirror is one-half of its radius of curvature.
When a clock is viewed in a mirror, the needles exhibit a time which appears to be 8:20. Then the actual time will be:
A point object is placed at a distance of 30 cm from a convex mirror of a focal length of 30 cm. What is the separation between the image and the object?
A convex lens of focal length 15 cm is placed coaxially in front of a convex mirror. The lens is 5 cm from the pole of the mirror. When an object is placed on the axis at a distance of 20 cm from the lens, it is found that the image coincides with the object. Calculate the radius of curvature of the mirror - (consider all-optical event):
