Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
following Figure shows two rays A and B being reflected by a mirror and going as A' and B'. The mirror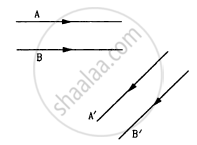
Options
is plane
is convex
is concave
may be any spherical mirror.
Solution
is plane
This is because the reflected rays are still parallel, which is only possible if the mirror is a plane mirror. A spherical mirror will either converge or diverge the reflected rays.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Calculate the distance of an object of height h from a concave mirror of radius of curvature 20 cm, so as to obtain a real image of magnification 2. Find the location of the image also.
Use the mirror equation to deduce that an object placed between the pole and focus of a concave mirror produces a virtual and enlarged image.
Using mirror formula, explain why does a convex mirror always produce a virtual image.
An object is kept on the principal axis of a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm. at a distance of 15
cm from its pole. The image formed by the mirror is:
(a) Virtual and magnified
(b) Virtual and diminished
(c) Real and magnified
(d) Real and diminished
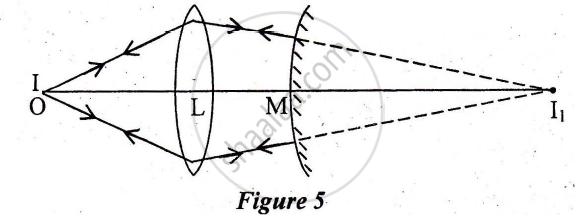
A point object O is placed at a distance of 15cm from a convex lens L of focal length 1 Ocm as shown in Figure 5 below. On the other side of the lens, a convex mirror M is placed such that its distance from the lens is equal to the focal length of the lens. The final image formed by this combination is observed to coincide with the object O. Find the focal length of the convex mirror
Define the term 'limit of resolution'?
Can a plane mirror ever form a real image?
Which of the following (referred to a spherical mirror) do (does) not depend on whether the rays are paraxial or not?
(a) Pole
(b) Focus
(c) Radius of curvature
(d) Principal axis
A light ray falling at an angle of 45° with the surface of a clean slab of ice of thickness 1.00 m is refracted into it at an angle of 30°. Calculate the time taken by the light rays to cross the slab. Speed of light in vacuum = 3 × 108 m s−1.
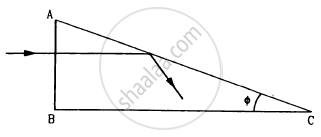
A light ray is incident normally on the face AB of a right-angled prism ABC (μ = 1.50) as shown in figure. What is the largest angle ϕ for which the light ray is totally reflected at the surface AC?
Find the maximum angle of refraction when a light ray is refracted from glass (μ = 1.50) to air.
Write any one use for each of the following mirrors :
(a) Convex
(b) Concave
For paraxial rays, show that the focal length of a spherical mirror is one-half of its radius of curvature.
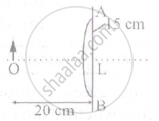
A point object is placed at a distance of 20 cm from a thin plano-convex lens of focal length 15 cm, if the plane surface is silvered. The image will form at:
A parallel beam of light is allowed to fall on a transparent spherical globe of diameter 30cm and refractive index 1.5. The distance from the centre of the globe at which the beam of light can converge is ______ mm.
The focal length f is related to the radius of curvature r of the spherical convex mirror by ______.
Car B overtakes car A at a relative speed of 40 ms-1. How fast will the image of car B appear to move in the mirror of focal length 10 cm fitted in car A, when car B is 1.9 m away from car A?
A point object is placed at a distance of 30 cm from a convex mirror of a focal length of 30 cm. What is the separation between the image and the object?
