Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
An object is kept on the principal axis of a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm. at a distance of 15
cm from its pole. The image formed by the mirror is:
(a) Virtual and magnified
(b) Virtual and diminished
(c) Real and magnified
(d) Real and diminished
Solution
Real and magnified
`1/u + 1/v =1/f`
u = -15, f = -10
`:. v = -30`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Using mirror formula, explain why does a convex mirror always produce a virtual image.
Define the term 'limit of resolution'?
A small object is placed at the centre of the bottom of a cylindrical vessel of radius 3 cm and height 4 cm filled completely with water. Consider the ray leaving the vessel through a corner. Suppose this ray and the ray along the axis of the vessel are used to trace the image. Find the apparent depth of the image and the ratio of real depth to the apparent depth under the assumptions taken. Refractive index of water = 1.33.
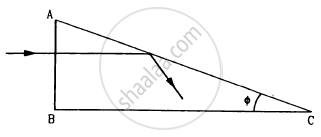
A light ray is incident normally on the face AB of a right-angled prism ABC (μ = 1.50) as shown in figure. What is the largest angle ϕ for which the light ray is totally reflected at the surface AC?
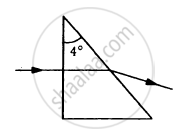
Find the angle of deviation suffered by the light ray shown in figure. The refractive index μ = 1.5 for the prism material.
Write any one use for each of the following mirrors :
(a) Convex
(b) Concave
A parallel beam of light is allowed to fall on a transparent spherical globe of diameter 30cm and refractive index 1.5. The distance from the centre of the globe at which the beam of light can converge is ______ mm.
The focal length f is related to the radius of curvature r of the spherical convex mirror by ______.
A point object is placed at a distance of 30 cm from a convex mirror of a focal length of 30 cm. What is the separation between the image and the object?
A convex lens of focal length 15 cm is placed coaxially in front of a convex mirror. The lens is 5 cm from the pole of the mirror. When an object is placed on the axis at a distance of 20 cm from the lens, it is found that the image coincides with the object. Calculate the radius of curvature of the mirror - (consider all-optical event):
