Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
An object is kept on the principal axis of a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm. at a distance of 15
cm from its pole. The image formed by the mirror is:
(a) Virtual and magnified
(b) Virtual and diminished
(c) Real and magnified
(d) Real and diminished
उत्तर
Real and magnified
`1/u + 1/v =1/f`
u = -15, f = -10
`:. v = -30`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Use the mirror equation to deduce that the virtual image produced by a convex mirror is always diminished in size and is located between the focus and the pole.
Use the mirror equation to deduce that an object placed between the pole and focus of a concave mirror produces a virtual and enlarged image.
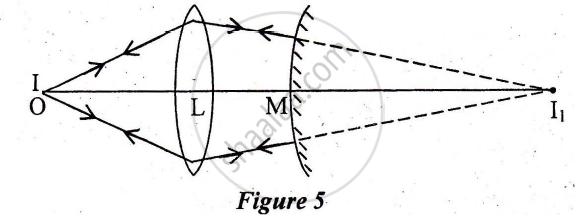
A point object O is placed at a distance of 15cm from a convex lens L of focal length 1 Ocm as shown in Figure 5 below. On the other side of the lens, a convex mirror M is placed such that its distance from the lens is equal to the focal length of the lens. The final image formed by this combination is observed to coincide with the object O. Find the focal length of the convex mirror
Define the term 'limit of resolution'?
following Figure shows two rays A and B being reflected by a mirror and going as A' and B'. The mirror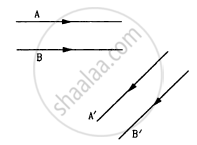
Mark the correct options.
Which of the following (referred to a spherical mirror) do (does) not depend on whether the rays are paraxial or not?
(a) Pole
(b) Focus
(c) Radius of curvature
(d) Principal axis
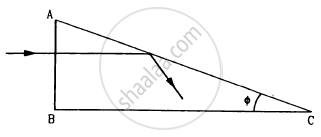
A light ray is incident normally on the face AB of a right-angled prism ABC (μ = 1.50) as shown in figure. What is the largest angle ϕ for which the light ray is totally reflected at the surface AC?
For paraxial rays, show that the focal length of a spherical mirror is one-half of its radius of curvature.
A point object is placed at a distance of 20 cm from a thin plano-convex lens of focal length 15 cm, if the plane surface is silvered. The image will form at: