Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A circular coil carrying a current I has radius R and number of turns N. If all the three, i.e. the current
I, radius R and number of turns N are doubled, then, the magnetic field at its centre becomes:
(a) Double
(b) Half
(c) Four times
(d) One fourth
उत्तर
Double
`B = (mu_0NI)/R`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
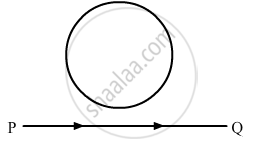
A conducting loop is held above a current carrying wire PQ as shown in the figure. Depict the direction of the current induced in the loop when the current in the wire PQ is constantly increasing.
A long straight wire in the horizontal plane carries a current of 50 A in north to south direction. Give the magnitude and direction of B at a point 2.5 m east of the wire.
A horizontal overhead power line carries a current of 90 A in east to west direction. What is the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field due to the current 1.5 m below the line?
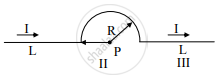
A conductor has three segments; two straights of length L and a semicircular with radius R. It carries a current I What is the magnetic field B at point P?
What is Lorentz force?
Show that currents in two long, straight, parallel wires exert forces on each other. Derive the expression for the force per unit length on each conductor.
A charged particle enters an environment of a strong and non-uniform magnetic field varying from point to point both in magnitude and direction, and comes out of it following a complicated trajectory. Would its final speed equal the initial speed if it suffered no collisions with the environment?
- perpendicular to direction of velocity of charged particle.
-
perpendicular to direction of magnetic field.
-
parallel to direction of velocity of charged particle.
-
parallel to the direction of magnetic field.
The magnetic moment of a current I carrying circular coil of radius r and number of turns N varies as ______.
A magnetic field exerts no force on
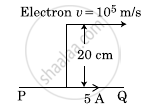
An infinitely long straight conductor carries a current of 5 A as shown. An electron is moving with a speed of 105 m/s parallel to the conductor. The perpendicular distance between the electron and the conductor is 20 cm at an instant. Calculate the magnitude of the force experienced by the electron at that instant.
A circular current loop of magnetic moment M is in an arbitrary orientation in an external magnetic field B. The work done to rotate the loop by 30° about an axis perpendicular to its plane is ______.
A charged particle of charge e and mass m is moving in an electric field E and magnetic field B. Construct dimensionless quantities and quantities of dimension [T]–1.
Two long current-carrying conductors are placed parallel to each other at a distance of 8 cm between them. The magnitude of the magnetic field produced at the mid-point between the two conductors due to the current flowing in them is 300µT. The equal current flowing in the two conductors is ______.
A beam of light travelling along X-axis is described by the electric field Ey = 900 sin ω(t - x/c). The ratio of electric force to magnetic force on a charge q moving along Y-axis with a speed of 3 × 107 ms-1 will be : [Given speed of light = 3 × 108 ms-1]
Distinguish between the forces experienced by a moving charge in a uniform electric field and in a uniform magnetic field. (Any two points)
