Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Show with the help of a labelled graph how their wavelength (λ) varies with their linear momentum (p).
Solution
The relation between λ and p is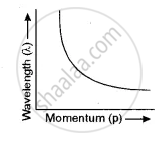
λ = `h/p`
Clearly, λ ∝ `1/p` i.e.; p increases λ decreases as shown by the graph.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What is the de Broglie wavelength of a bullet of mass 0.040 kg travelling at the speed of 1.0 km/s?
For what kinetic energy of a neutron will the associated de Broglie wavelength be 1.40 × 10−10 m?
Obtain the de Broglie wavelength of a neutron of kinetic energy 150 eV. As you have an electron beam of this energy is suitable for crystal diffraction experiments. Would a neutron beam of the same energy be equally suitable? Explain. (mn= 1.675 × 10−27 kg)
A proton and α-particle are accelerated through the same potential difference. The ratio of the de-Broglie wavelength λp to that λα is _______.
The de-Broglie wavelength associated with a material particle when it is accelerated through a potential difference of 150 volt is 1 Å. What will be the de-broglie wavelength associated with the same particle when it is accelerated through a potential difference of 4500 V?
An electron (mass m) with an initial velocity `v = v_0hati` is in an electric field `E = E_0hatj`. If λ0 = h/mv0, it’s de Broglie wavelength at time t is given by ______.
Relativistic corrections become necessary when the expression for the kinetic energy `1/2 mv^2`, becomes comparable with mc2, where m is the mass of the particle. At what de Broglie wavelength will relativistic corrections become important for an electron?
- λ = 10 nm
- λ = 10–1 nm
- λ = 10–4 nm
- λ = 10–6 nm
The equation λ = `1.227/"x"` nm can be used to find the de Brogli wavelength of an electron. In this equation x stands for:
Where,
m = mass of electron
P = momentum of electron
K = Kinetic energy of electron
V = Accelerating potential in volts for electron
The ratio of wavelengths of proton and deuteron accelerated by potential Vp and Vd is 1 : `sqrt2`. Then, the ratio of Vp to Vd will be ______.
A particle of mass 4M at rest disintegrates into two particles of mass M and 3M respectively having non zero velocities. The ratio of de-Broglie wavelength of particle of mass M to that of mass 3M will be:
